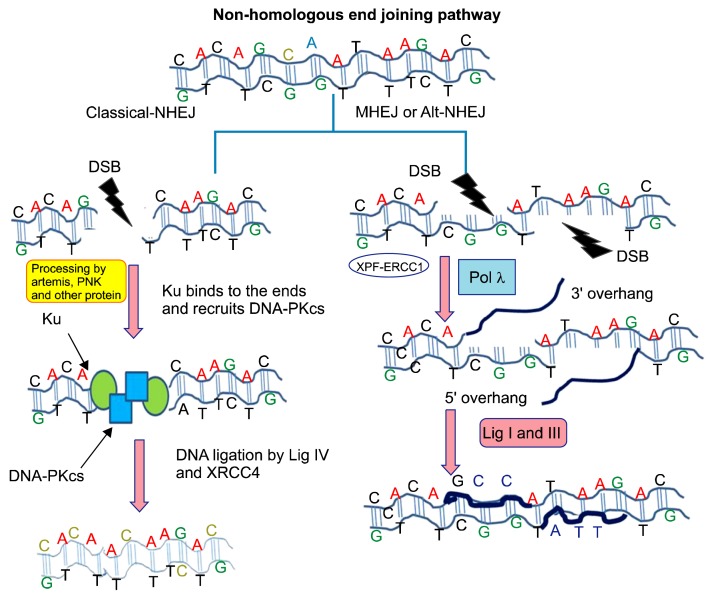
Figure 2.
This figure illustrates the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair pathway. In the classical NHEJ pathway, after the formation of the DSB, the Ku complex is recruited. Subsequently, proteins such as DNA dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) ultimately lead to blunt double-strand ligation through the help of DNA ligase IV and X-ray repair cross complementing 4 (XRCC4), which seals the DSB. In the alternative NHEJ pathway, the DSB is processed by ERCC excision repair 1 (ERCC1) and DNA polymerase gamma. In the next step, ligation is completed by DNA ligase I and DNA ligase III to fill the DSB gap.