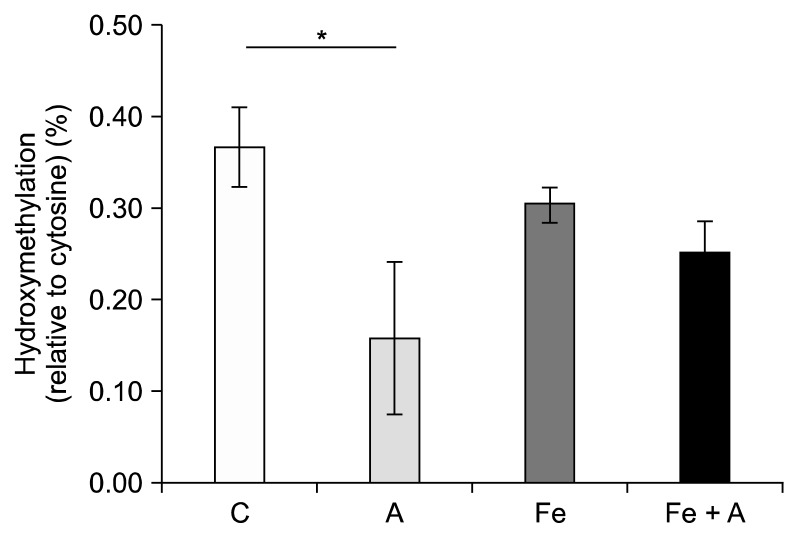
Figure 5.
Influence of iron supplementation on DNA hydroxymethylation reduced by chronic alcohol consumption. A significant decrease in DNA hydroxymethylation was seen in rats fed the alcohol diet without iron relative to the control group (P = 0.03). When rats were fed a diet containing both alcohol and iron, the percent hydroxymethylation was equivalent to the rats fed a control diet with or without iron. Values are averages and SE (n = 6 per group). C, Lieber-DeCarli control diet (0% calorie from ethanol); A, Lieber-DeCarli alcohol diet (36% calories from ethanol); Fe, Lieber-DeCarli control diet (0% calorie from ethanol) with iron supplementation (0.6% carbonyl iron); Fe + A, Lieber-DeCarli alcohol diet (36% calories from ethanol) with iron supplementation (0.6% carbonyl iron). *Statistically significant at a P < 0.05.