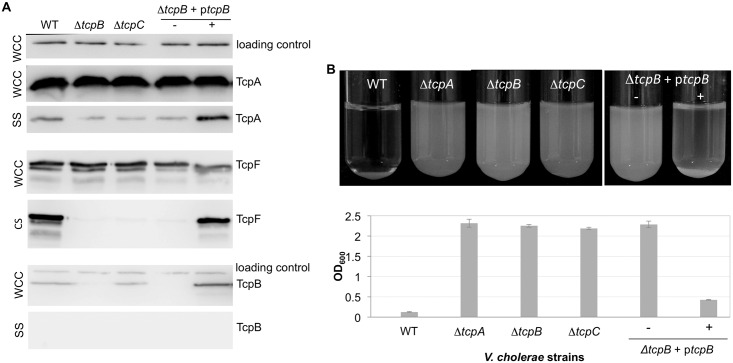
Fig 3. V. cholerae requires TcpB for efficient pilus assembly and functions.
(A) Immunoblots of V. cholerae whole cell culture (WCC), sheared culture supernatant (SS) and cleared culture supernatant (CS) fractions probed with antibodies against TcpA, TcpF and TcpB, as indicated by the labeled protein bands. SS for the TcpA and TcpB blots was prepared by homogenizing the cells to shear the pili then removing intact cells by centrifugation. The SS fractions were topped up with PBS to a volume matching that of the WCC, and equal volumes (25 ul) of each sample were loaded onto the gel. TcpA in the SS fraction of the ΔtcpB and ΔtcpC mutants may represent contamination from cell membranes due to the shearing method or membrane blebbing due to high levels of TcpA that accumulate in the inner membrane. Secreted TcpF is detected in the CS fraction, obtained by removing V. cholerae cells by centrifugation and filtration without shearing. TcpF often appears as a doublet in immunoblots. The lower band of the doublet appears to be a proteolysed form of TcpF lacking the N-terminal ~25 amino acids. This segment is not resolved in the TcpF crystal structure suggesting it is flexible, which may explain its protease sensitivity [10]. The ΔtcpB strain is complemented with ptcpB without (-) and with (+) 0.001% rhamnose inducer. The loading control is an unknown ~60 kDa protein present in the WCC fraction and detected by the Strep-Tactin-HRP conjugate. (B) V. cholerae autoagglutination as a function of TcpB expression. Cell cultures are shown after overnight growth followed by 15 min stationary incubation at room temperature (top panel). The OD600 of the culture supernatant after the cells have settled is plotted for each sample in the bottom panel. The more complete the autoagglutination the lower the OD600 value. Values are averaged for 3 experiments; error bars represent standard deviations.