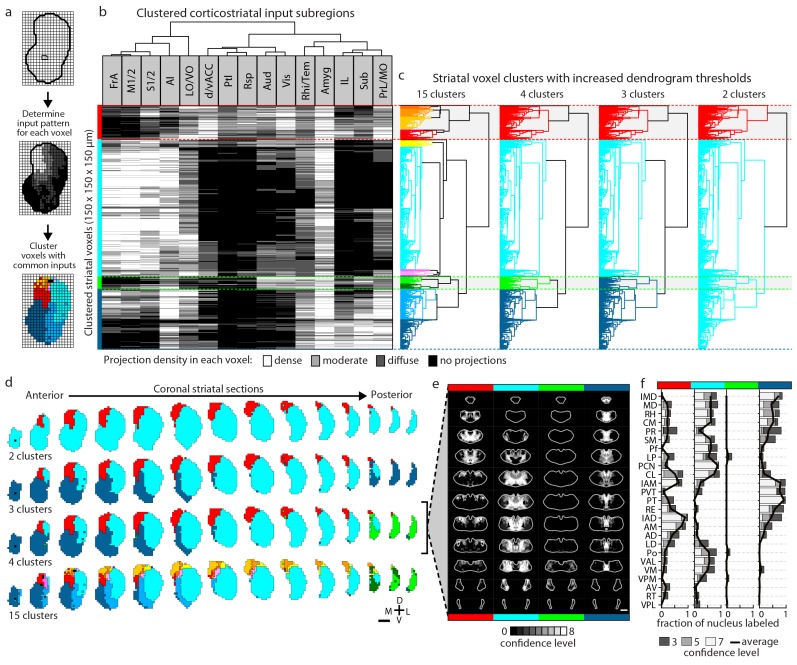
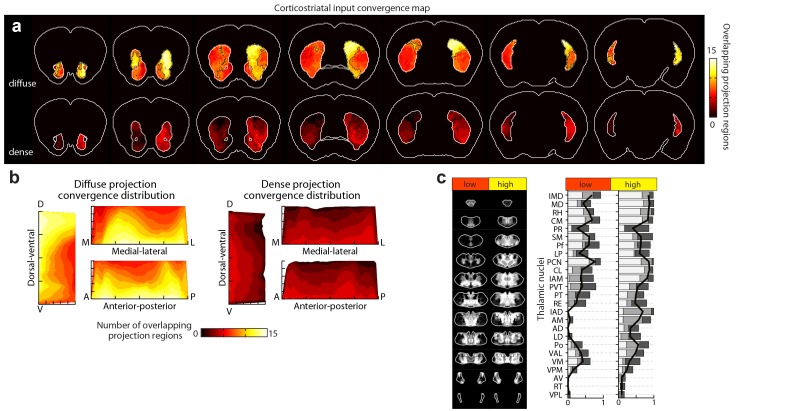
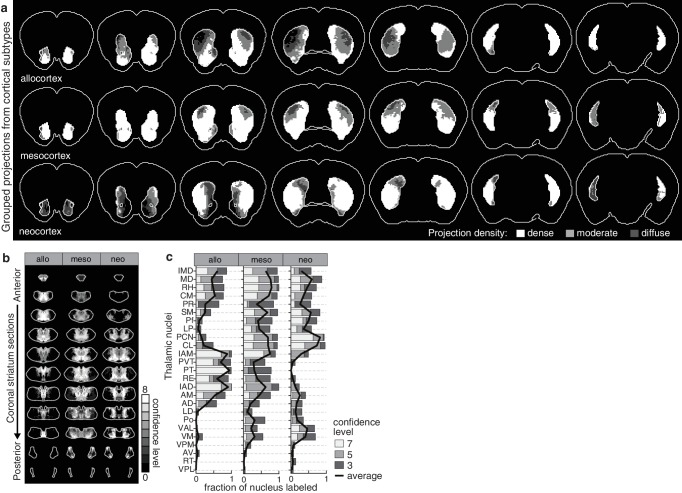
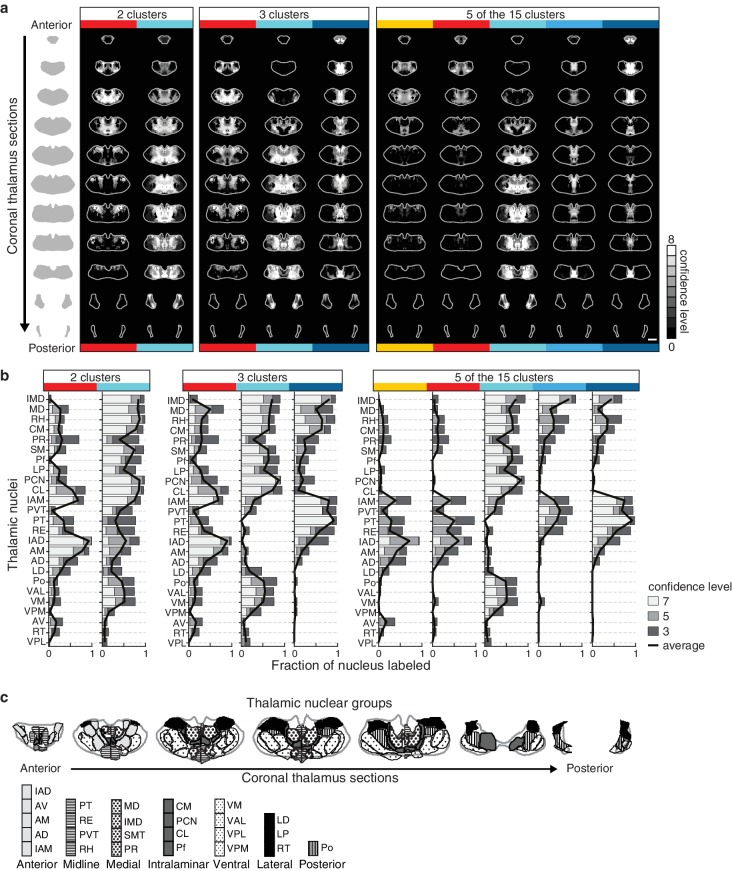
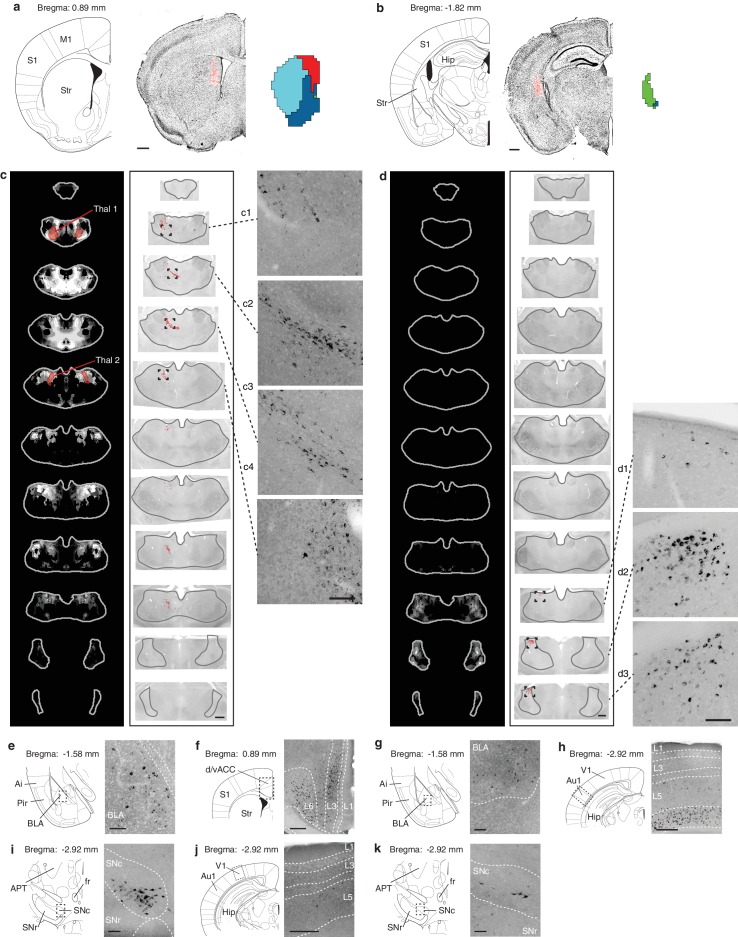
Figure 5. Striatal subdivisions based on cortical input convergence.
(a) Schematic of voxel clustering method. The striatum was downsampled into 150 µm × 150 µm × 150 µm voxels (top panel), the projection density (dense, moderate, or diffuse) to each voxel was determined for inputs from each cortical subregion (middle panel), and the sum of this information was used to cluster voxels with common inputs (bottom panel). (b) All striatal voxels (rows) were hierarchically clustered based on their cortical input patterns, and cortical subregions (columns) were clustered based on common innervation patterns to the striatum. The projection densities in each voxel are indicated in gray scale, as determined in Figure 2b. (c) Four separate thresholds were applied to the voxel dendrogram to produce 2, 3, 4, and 15 clusters. The cluster boundaries (dotted color lines) for the threshold producing four clusters are carried across the clustered voxels in panel b. Clusters containing only one voxel were ignored in our analyses. (d) Coronal sections outline the ipsilateral (according to the injection hemisphere) striatum, starting 1.8 mm anterior to bregma and continuing posterior in 300 µm steps, showing the spatial location of the clusters determined in panel c. (e) Thalamic confidence maps indicating the thalamic origins of thalamostriatal projections to the four striatal subdivisions defined by cluster analysis in panel d (thalamic section positions are the same as in Figure 4a). The method used to localize the origin of thalamic projections was similar to that described for Figures 3 and 4, except that differences in the data resulted in an eight level confidence maps based on the inclusion of each injection in each of four groups (see Materials and methods). (f) The fraction of each thalamic nucleus covered by confidence levels 3, 5, and 7 (dark, medium and light gray bars, respectively), with their average (black line) shown for the confidence maps in panel e (see Figure 5—figure supplement 3 for full dataset, and Materials and methods for details).