Figure 1.
Molecular Organization and Expression Analysis of BRK1, NAPP, and PIRP and Characterization of napp and pirp Mutants.
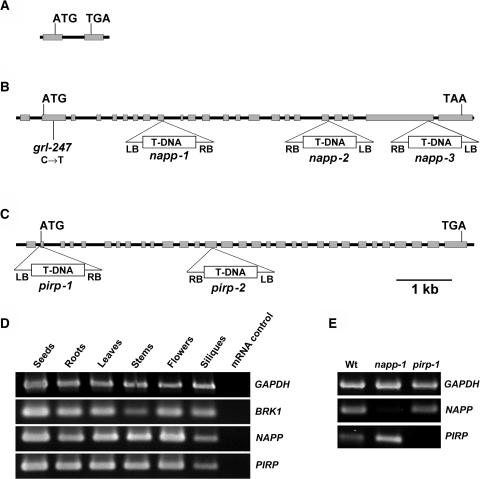
(A), (B), and (C) Gene structure and location of mutations in BRK1 (A), NAPP (B), and PIRP (C). Gray boxes represent exons, and black lines represent introns and untranscribed flanking sequences. The location and orientation of T-DNA insertions in NAPP and PIRP are shown. grl-247 is an ethyl methanesulfonate–generated allele.
(D) RT-PCR analysis of NAPP, PIRP, and BRK1 expression in various tissues. mRNA was extracted from different parts of Arabidopsis plants and used for RT-PCR analysis as described in the text. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as a positive control. mRNA not subjected to reverse transcription was used as a negative control for each gene.
(E) RT-PCR analysis of NAPP and PIRP expression in wild-type napp-1 and pirp-1. mRNA was extracted from leaves of soil-grown wild-type plants and homozygous mutant plants and subjected to RT-PCR. GAPDH was used as a positive control.