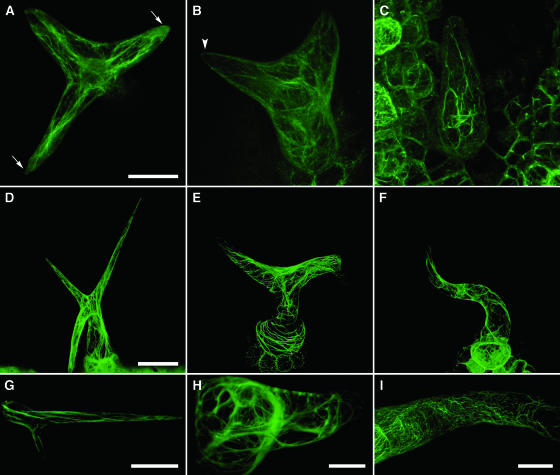
Figure 8.
Organization of F-Actin in Leaf Trichomes of Wild-Type, napp-1, and pirp-1 Plants.
F-actin was visualized by stable expression of YFP-mTalin in 8-d-old plants ([A] to [C]) and 9-d-old plants ([D] to [F]) and by transient expression in 14-d-old plants ([G] to [I]). Young ([A] to [C]) and mature ([D] to [I]) trichomes were imaged using confocal microscopy. Three-dimensional projections were generated from multiple optical sections.
(A) A young wild-type trichome with elongating branches. Actin filaments are longitudinally oriented; two of the branch tips are dominated by diffuse actin.
(B) A pirp-1 trichome at a similar stage of development as in (A). Actin filaments show a more random orientation but not increased bundling. Diffuse actin is not observed in the branch tips.
(C) A pirp-1 trichome at a slightly later stage contains thick actin cables extending both longitudinally and transversely across the branch.
(D) A (mature) wild-type trichome showing a fine network of longitudinally oriented actin filaments.
(E) A pirp-1 trichome with thick actin cables that are mainly transversely oriented, especially in the radially expanded stalk. Note the high density of actin filaments at the branch point between the two branches.
(F) A napp-1 trichome showing transversely oriented filaments.
(G) A branch of a wild-type trichome with a population of diffuse actin at the branch tip.
(H) A transverse cross section through a pirp-1 trichome. Thick actin cables extend across the stalk. The branch tip has small amounts of both actin filaments and diffuse actin.
(I) Portion of the branch of a moderately affected napp-1 trichome. Thick actin cables are not seen, but actin filaments show varying degrees of transverse orientation.
Bars = 20 μm in (A) to (C), (H), and (I), 50 μm in (D) to (F), and 40 μm in (G).