Fig. 1.
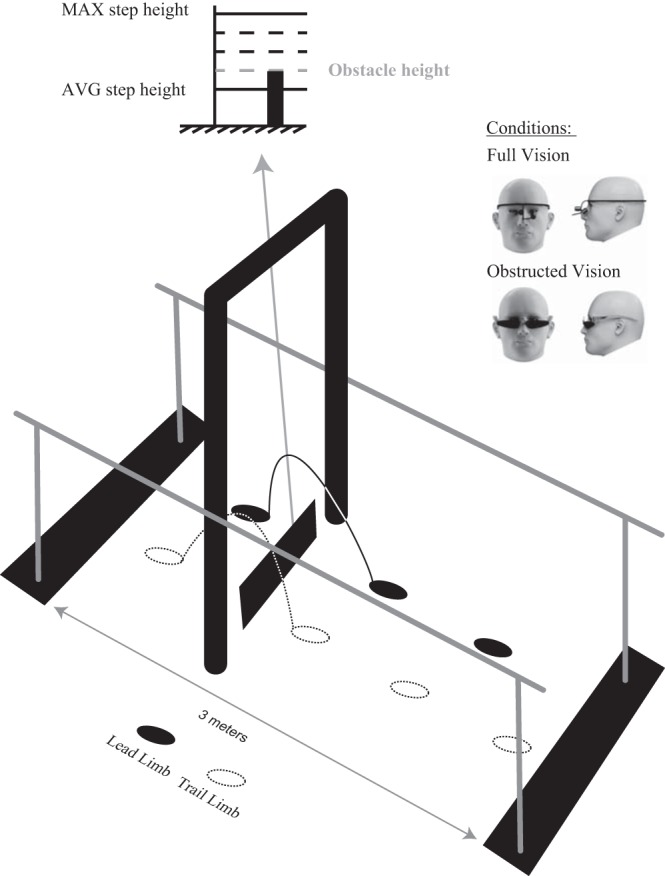
Experimental setup. Participants walked between parallel bars and were asked to step over an obstacle positioned between a doorframe (indicating its spatial location) under full and obstructed vision conditions. Obstacle height for each subject was set at a level corresponding to average peak toe height during usual stepping plus 25% of the difference in peak toe height between maximum and usual stepping of the stronger limb [subjects with spinal cord inujry (SCI)] or dominant limb [ able-bodied (AB) subjects].
