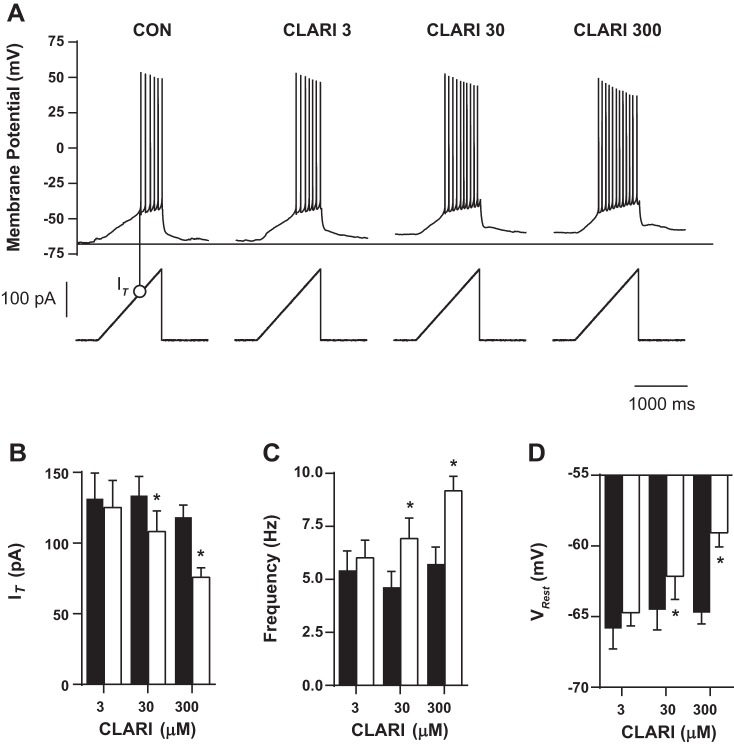
Fig. 2.
Clarithromycin-induced hyperexcitability is dose dependent. A: characteristic voltage responses (top) to an injected current ramp (bottom). Minimum injected ramp current initializing action potentials was measured. Action potential threshold current (IT) is designated for the control experiment by a thin vertical line with an open circle and summarized in B. Horizontal line indicates level of VRest in control conditions (CON). B–D: neurons were exposed to different clarithromycin concentrations. Each neuron was also exposed to control conditions and acts as its own control. Bar graph pairs represent average values ± SE in controls (filled bars) and in clarithromycin (open bars). Doses of 30 and 300 μM clarithromycin significantly affected neuronal firing expressed as IT (CON vs. CLARI 3: n = 7, CON vs. CLARI 30: n = 12, CON vs. CLARI 300: n = 20; paired t-test, P = 0.2, *P = 0.002, *P = 0.0001, respectively), frequency (n = 7, n = 12, n = 20; paired t-test, P = 0.1, *P = 0.003, *P < 0.0001), and depolarized VRest (n = 7, n = 13, n = 21; paired t-test, P = 0.3, *P = 0.04, *P < 0.0001).