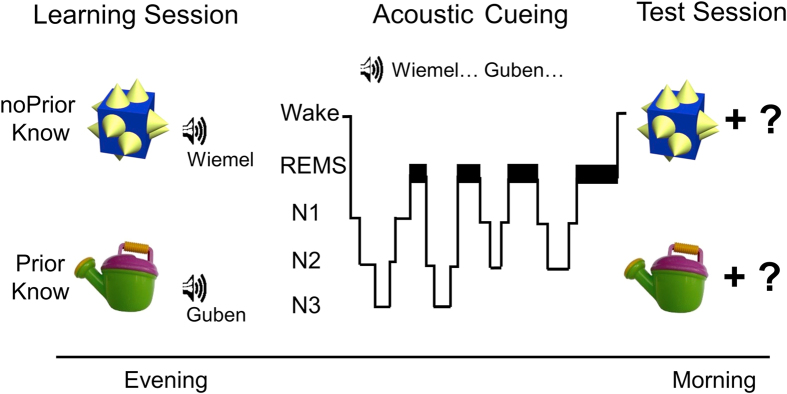
Figure 1. Task and design.
In the learning session in the evening, participants encoded associations of acoustically presented pseudo-words and visually presented familiar objects (stimuli related to prior knowledge, “PriorKnow”) and novel objects (stimuli not related to prior knowledge, “noPriorKnow”). Half of the words from both conditions were presented again during post-learning NonREM sleep (stage N2 and N3) in order to induce the reactivation of the associated information. A typical polysomnogram visualizes the proportion of sleep stages during the nocturnal retention interval (wake (W), non-rapid eye movement (NonREM) sleep stages 1–3 (N1–N3), REMS). In the Test Session the next morning, memory recall was tested for all picture-word associations in a cued recall procedure.