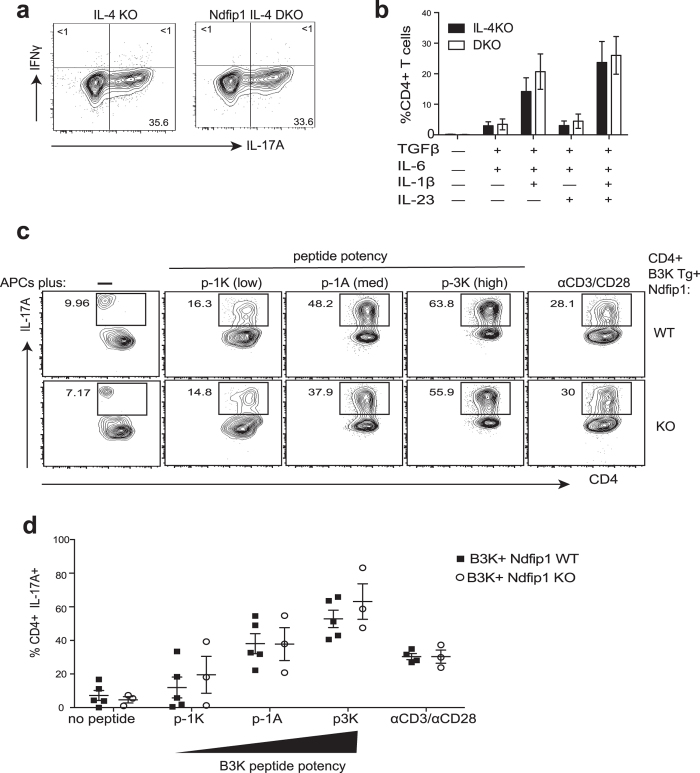
Figure 2. Ndfip1 does not limit the differentiation of Th17 cells in vitro.
(a,b) Naïve sorted CD4+ T cells from IL-4 KO or Ndfip1 IL-4 DKO animals were cultured under various Th17-polarizing conditions for 5 days as noted. (a) Representative Th17 differentiation using IL-1β, IL-23, TGFβ, and IL-6. (b) Average percentages of Th17 cells generated with different combinations of TGFβ, IL-6, IL-1β and IL-23. (c,d) Peptide pulsed APCs were used to stimulate B3K transgenic T cells. T cells from Ndfip1 KO RAG1−/− B3K+ or RAG1−/− B3K+ control animals were incubated with APCs pulsed with peptides of low (p-1K), medium (p-1A) or high (p-3K) TCR-stimulating potency for 5 days under Th17 polarizing conditions. Cells were then restimulated and analyzed using flow cytometry. (c) Representative plots showing Th17 generation using no peptides, the three altered peptide ligands, or with antiCD3/anti CD28 are shown for comparison. (d) Combined data for multiple experiments illustrating Th17 generation, with each dot representing one mouse (c). In (a,b) data is shown for n = 5 animals per group in at least three independent experiments, and statistical significance was tested using a using 2-way ANOVA. Panels c-d, include data from 2 independent experiments, and the combined data was analyzed using 2-way ANOVA. All error bars represent mean +/− SEM.