Table 1.
Examples of activities with the X is like Y heuristic.
| Example of modeling | |
| The adult read the sentence:“Skyscrapers are the city's giraffes” | |
Strategy 1: “Is like strategy”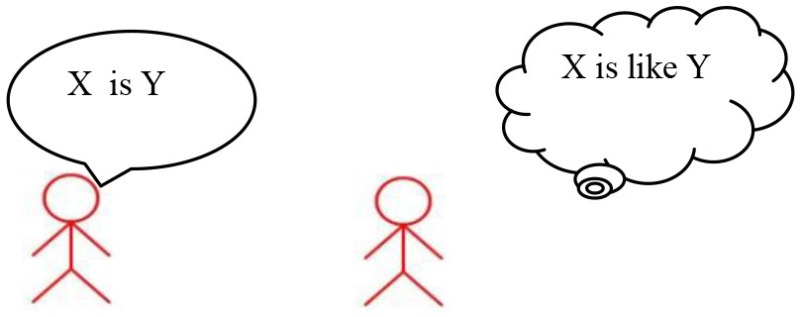
|
If someone says “skyscrapers are the city's giraffes,” people who listen to that sentence know that skyscrapers simply cannot be giraffes. Skyscrapers are buildings and giraffes are animals. But, to understand what is meant by this sentence I may use my first strategy with cards. I will replace X with Y and add “is like.” Then, the sentence becomes skyscrapers are like giraffes. |
Strategy 2: Comparative strategy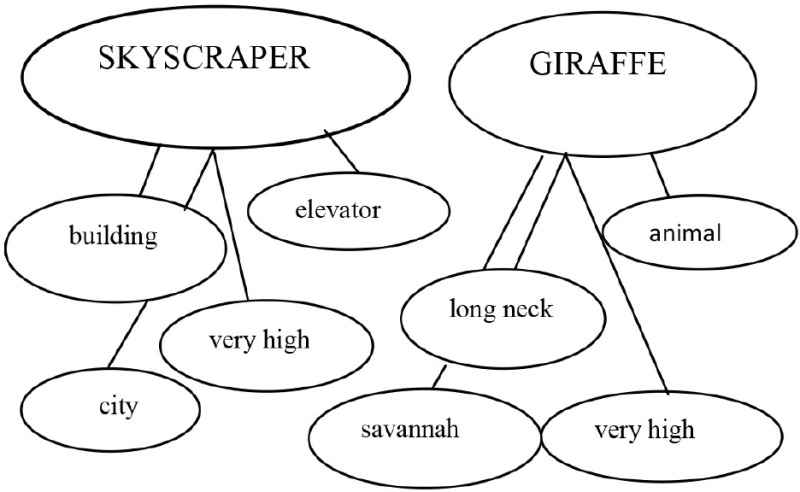
|
Now, I will use my second strategy. I'll be thinking of the characteristics of the skyscrapers and write them down here in my thinking map. Then, I'll write that skyscrapers are buildings, that they are very high, they have elevators, etc. Now, it's giraffes' turn. I'll be thinking of the characteristics of the giraffes and write them down in my map. Giraffes are animals, they are very high, have a long neck, they live in savannahs, etc. Right. Now, I'll see which characteristics are appropriate for both skyscrapers and giraffes. For instance, “building” is appropriate for skyscraper but has nothing to do with giraffes, then I'll reject it…….”Very high” goes for both, then, I'll accept it as an appropriate characteristic. Skyscrapers and giraffes are both very high. |
| Metalinguistic reflection | Then, we may state that the guy who said “skyscrapers are giraffes” actually meant that skyscrapers are the highest buildings in a city just as giraffes are the highest animals in a savannah. The word “giraffe” replaces another one, in this case “very high,” because it expresses the meaning of being very high. |
| Example of joint construction | |
Strategy 1: “Is like strategy”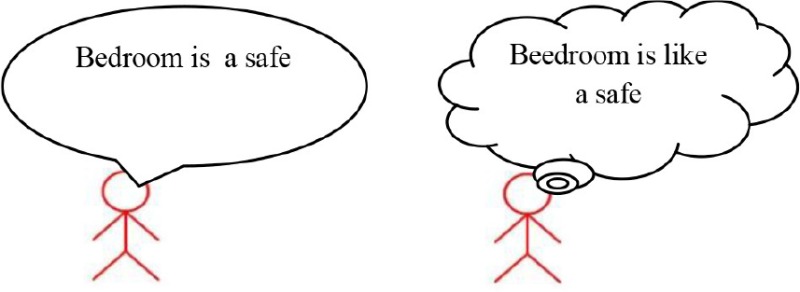
|
Adult: “What does this sentence mean: Bedroom is a safe ?” M.M. “Bedroom is like a safe” Adult: “Ok, shall we use strategy 1 and write down the new sentence in the bubble ?” |
Strategy 2: Comparative strategy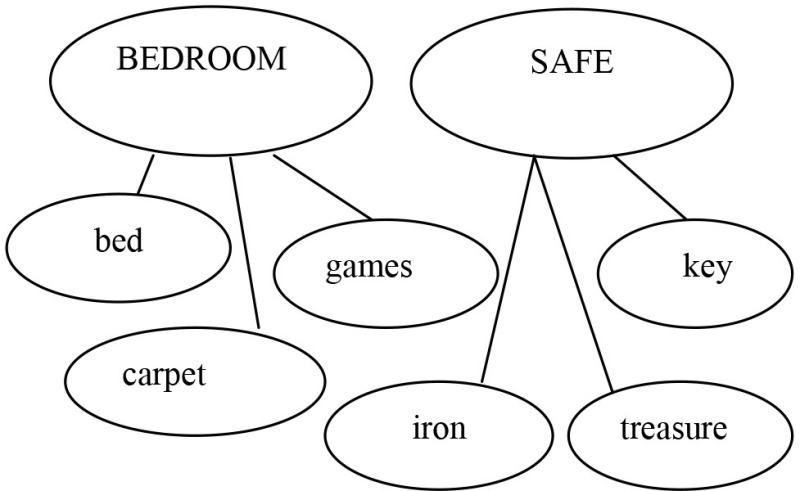
|
Adult: “Now we can say all we know about safes.” M.M.: “It can be iron made, and there can be money or jewelery inside. You can open it with a key or a code. Pharaons used to have the room of treasure, like Sethi in the Kings' Valley.” The adult invited M.M. to write down these features in the bubbles of the thinking map. M.M. wrote IRON, KEY, CODE, MONEY, TREASURE for the word Safe and BED, CARPET, GAMES for the word Bedroom. MM. was asked to select characteristics that can be common to Bedroom and Safe. M.M. selected KEY and discarded every other feature except TREASURE. M.M.: “A bedroom can have treasures.” Adult: “Treasures like those of Sethi”? M.M.: “No, perhaps a precious collection of shells, marbles or bus tickets. Nobody has to touch them, as with a safe.” |
| Metalinguistic reflection | Adult and M.M. came to the conclusion that a bedroom is a suitable place where to keep precious objects. |
| Example of autonomous activity | |
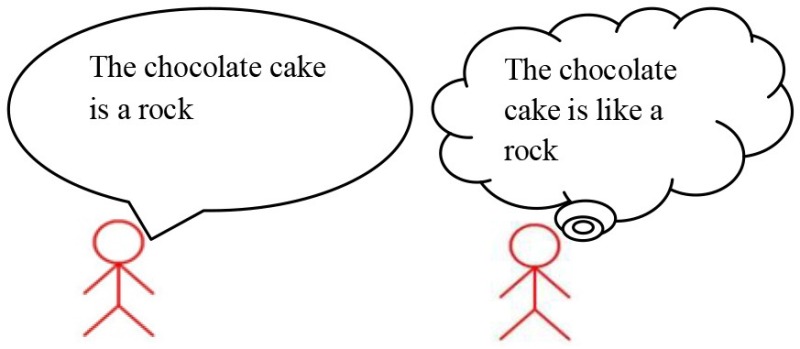 |
“The chocolate cake is a rock” The child had to insert the sentence in the bubbles using strategy 1 (written exercise) like in the example in the left column. |
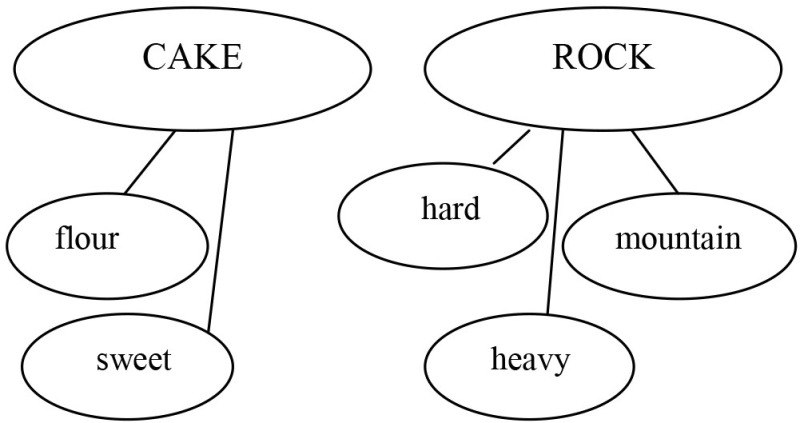 |
The child had to build the thinking map with CAKE and ROCK (written exercise) like in the example in the left column. |
| Metalinguistic reflection (oral discussion) | Adult: “What does it mean, then, that the chocolate cake is a rock?” M.M.: “Well, it means that the cake is dried, tough, you really cannot eat it.” |
