Fig. 7.
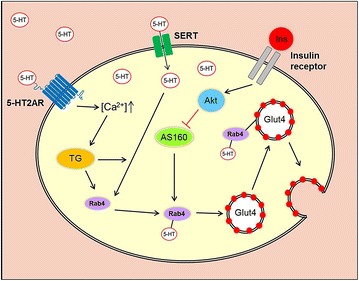
Our proposed model of 5-HT-induced translocation of GLUT4 vesicles to the cell membrane of 5-HT-stimulated skeletal muscle cells (based on previous research performed by Paulmann et al. [7] ]: Initially, extracellular 5-HT enters the cell via the 5-HT re-uptake transporter (SERT) while Ca2 + influx increases via activation of the 5-HT2A-receptor (5-HT2AR) by 5-HT binding. Among other functions, Ca2 + activates the transglutaminase (TG) which serotonylates a variety of intracellular proteins. In skeletal muscle cells, Rab4, which plays an important role in the translocation of GLUT4 to the cell membrane, becomes serotonylated and, thereby, activated. Consequently, glucose uptake into the cell increases. Activation of the insulin receptor resulting in inhibition of AKT-substrate 160 (AS160) also leads to the activation of Rab4 proteins indirectly
