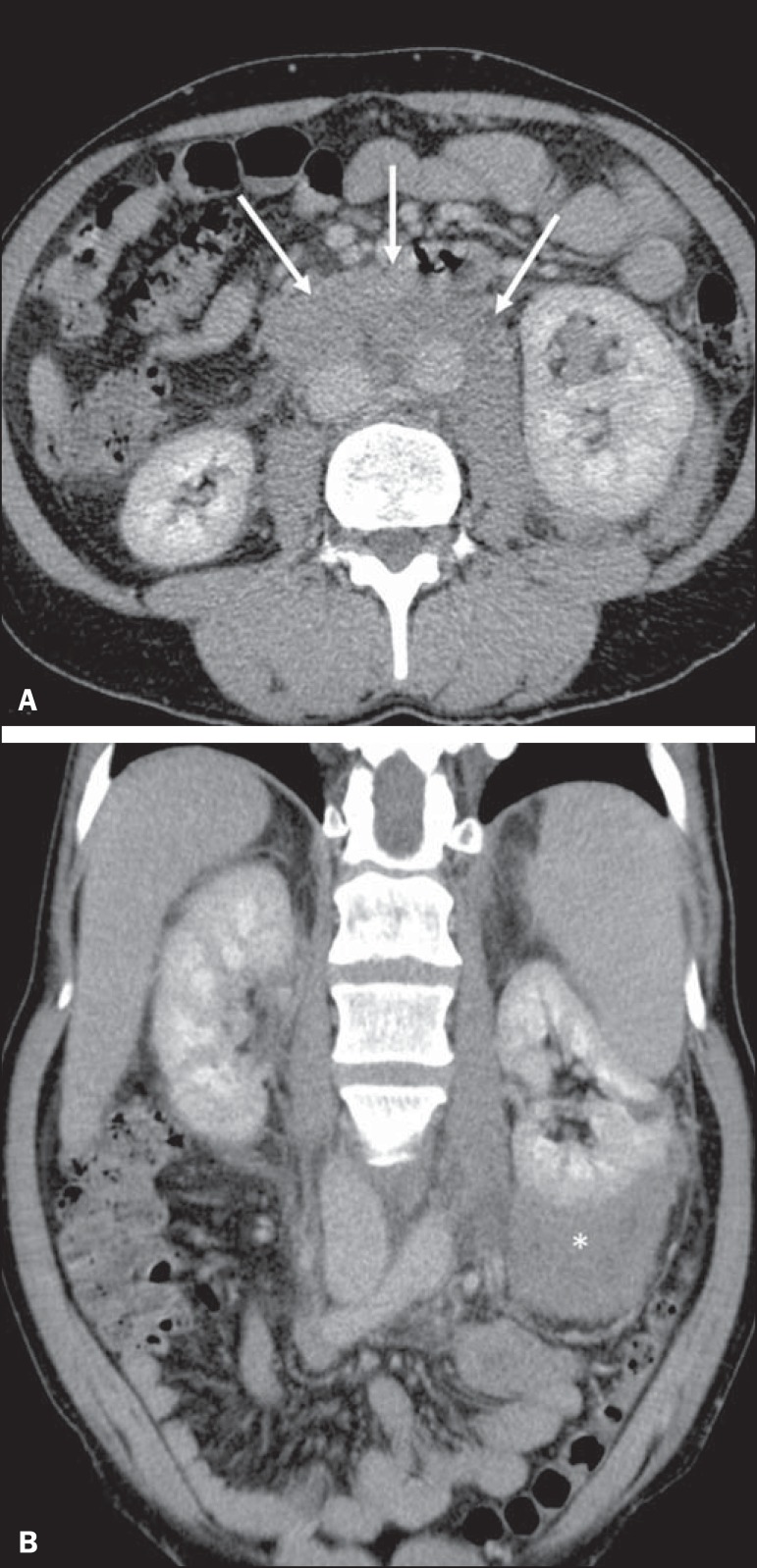
Figure 15.
Contiguous renal invasion in retroperitoneal disease. Contrast-enhanced CT of the abdomen, in the axial plane (A) and in coronal reconstruction (B), showing extensive retroperitoneal lymph node involvement (arrows) and a hypovascularized mass encompassing the inferior pole of the left kidney (asterisk). The symmetrical pattern of contrast uptake indicates that there was no compression of the parenchyma or impairment of renal function in the affected kidney.