Figure 9. A model illustrating the mechanism by which proteasome inhibitors (PIs) selectively kill GSCs.
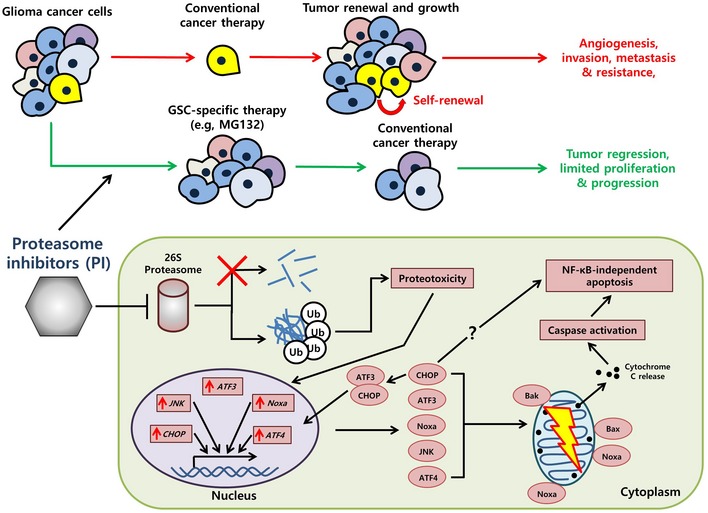
A key factor in low‐dosage proteasome inhibition and its selective efficacy against GSCs lies in the sustained accumulation of ubiquitinated conjugates due to the failure of the proteasome (red cross). The resulting proteotoxicity then can activate the apoptotic cascade, among which genes such as ATF3, CHOP, and JNK are upregulated and translated into their respective protein counterparts. ATF3 and CHOP also form a heterodimer which serves to maintain the apoptotic cascade. The ATF3‐CHOP axis‐induced cell death is independent of classical ER stress‐associated apoptosis and may instead directly play a role via NOXA to induce mitochondrial dysfunction (yellow lightning) and eventually cell death.
