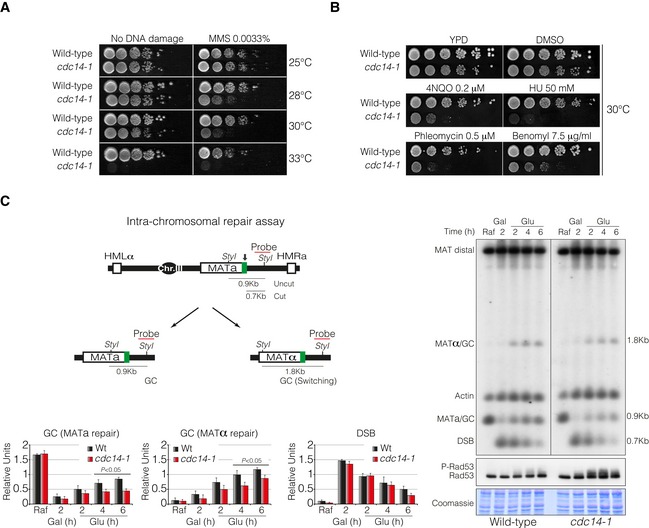
Tenfold serial dilutions from overnight cultures of wild‐type and cdc14‐1 cells dropped and grown on solid rich media or media containing MMS at 25, 28, 30 or 33°C. Note that cdc14‐1 cells exhibit growth sensitivity to MMS at 28 and 30°C compared to wild‐type cells.
Tenfold serial dilution from mid‐log phase cultures of wild‐type and cdc14‐1 cells grown on solid rich media or media containing mock DMSO (as non‐treated control), 4NQO, HU, phleomycin and benomyl at 30°C. Note that cdc14‐1 cells present a marked sensitivity to all DNA damage agents tested.
Left panel: Schematic representation showing relevant genomic structure of the strain used to assess intra‐chromosomal repair. The location of a MAT‐specific probe and the restriction endonuclease cleavage sites used for Southern blot analysis to detect repair product formation are indicated. Arrow depicts the localization of the double‐strand break. Right panel: Physical analysis of intra‐chromosomal repair in wild‐type and cdc14‐1 cultures at the semipermissive temperature. After DSB formation by the expression of the HO, glucose was added to repress it, thus allowing repair with HM donor sequences. Genomic DNA was digested with StyI, separated on agarose gel and blotted. Blots were hybridized with a probe corresponding to the MATa‐distal sequence. A second probe for the actin gene was used to control the amount of genomic DNA loaded at each time point. Immunoblot analysis of Rad53 during mating‐type switching experiments is shown. Coomassie blue staining is depicted as a loading control. Graphs show quantification of gene conversion (GC) leading to the re‐establishment of MATa or switching to MATα and DSB formation. The data were normalized with the actin as a loading control. Graphs show the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Replicates were averaged and statistical significance of differences assessed by a two‐tailed unpaired Student's t‐test.
Data information: MMS, methyl methanesulphonate; DMSO, dimethyl sulphoxide; 4NQO, 4‐nitroquinoline‐1‐oxide; HU, hydroxyurea; Raf, raffinose; Gal, galactose; Glu, glucose; DSB, double‐strand break; GC, gene conversion.
Source data are available online for this figure.