Figure 1.
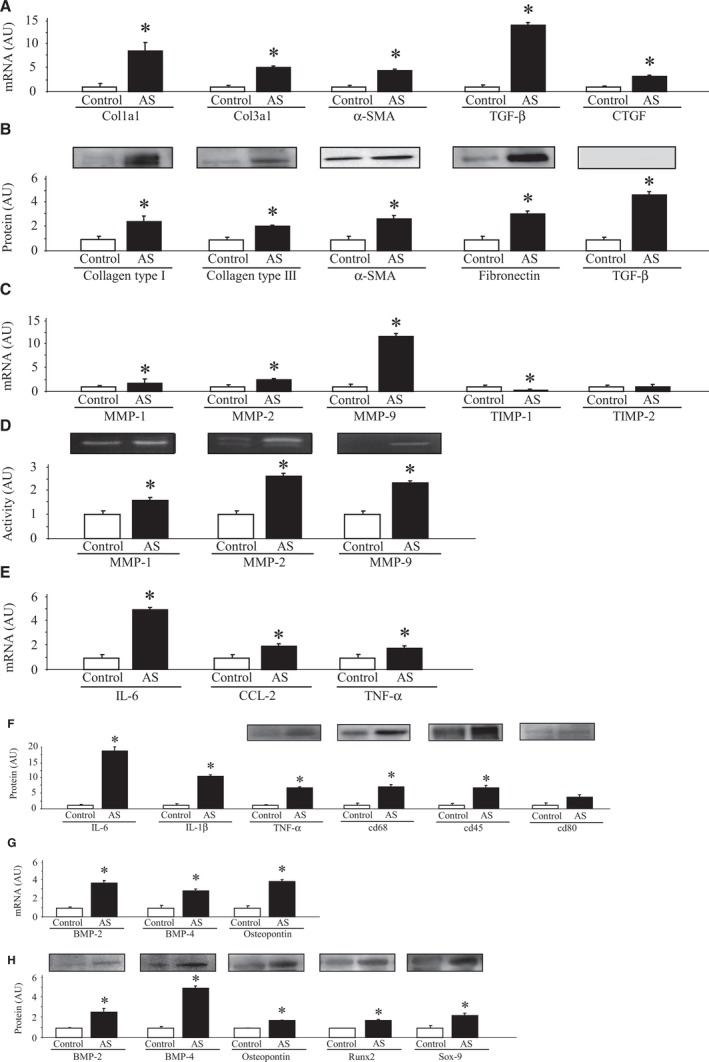
Fibrosis, inflammation, and calcification in AS valves compared to controls. ECM components in AVs at mRNA (A) and protein (B) levels. mRNA levels of MMPs and its inhibitors (TIMPs) in AVs (C). MMPs activities in controls and AS valves (D). Inflammatory markers were measured in stenotic and control AVs at mRNA (E) and protein (F) levels. mRNA levels of calcification markers in AVs (G) and protein expressions of calcification markers in AVs (H). All conditions were performed at least in triplicate. Histogram bars represent the mean±SEM of each group of subjects (control n=11 and patients with severe calcific AS n=77) in arbitrary units (AU) normalized to HPRT and stain‐free gel for cDNA and protein, respectively. *P<0.05 versus control group. AS indicates aortic stenosis; AVs, aortic valves; BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; CCL2, C‐C motif chemokine ligand 2; Col1a1, collagen type I alpha 1 chain; Col3a1, collagen type III alpha 1 chain; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; ECM, extracellular matrix; HPRT, hypoxanthine‐guanine phosphoribosyltransferase; IL, interleukin; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; Runx2, runt‐related transcription factor 2; Sox‐9, SRY (sex‐determining region Y)‐box 9; α‐SMA, alpha‐smooth muscle actin; TGF‐β, transforming growth factor beta; TIMPs, tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor alpha.
