Figure 3.
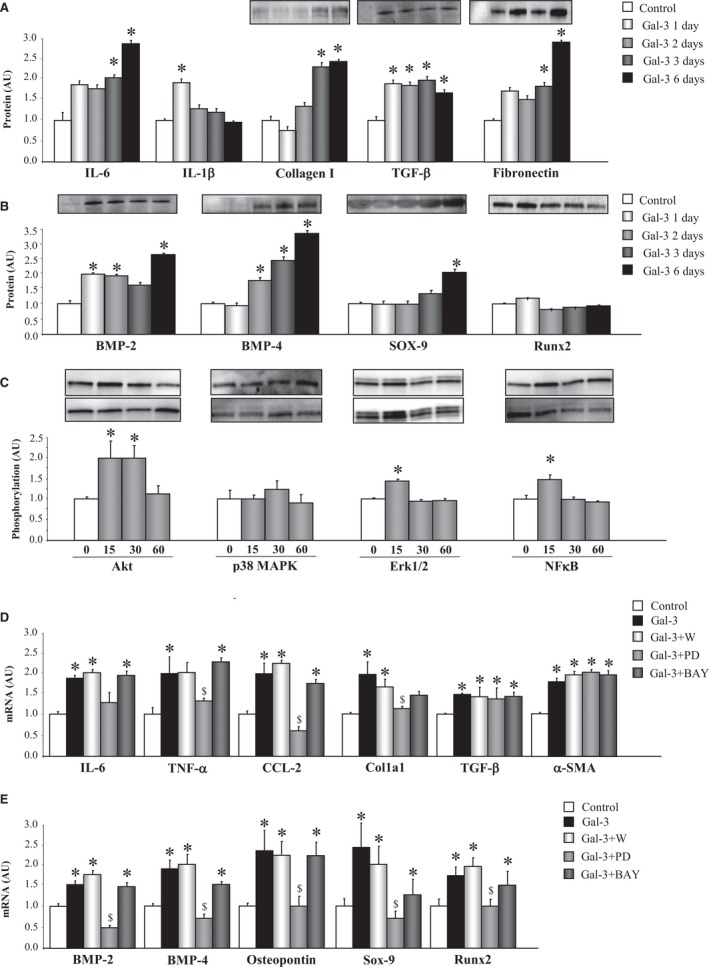
Gal‐3 induces inflammation, ECM components, and calcification markers in VICs. Effects of Gal‐3 on inflammatory markers, ECM components (A), and calcification markers (B) in VICs. Effects of Gal‐3 on phosphorylation of intracellular pathways in VICs (C). Effects of cell signaling chemical inhibitors on the proinflammatory and profibrotic effect of Gal‐3 in VICs (D). Effects of cell signaling chemical inhibitors on the pro‐osteogenic effect of Gal‐3 in VICs (E). All conditions were performed at least in triplicate. Histogram bars represent the mean±SEM of 6 assays in arbitrary units (AU) normalized to stain free for protein and to β‐actin and HPRT for cDNA. *P<0.05 versus control; $ P<0.05 vs Gal‐3. Akt indicates protein kinase B; BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; CCL2, C‐C motif chemokine ligand 2; Col1a1, collagen type I alpha 1 chain; ECM, extracellular matrix; ERK1/2, extracellular signal‐regulated kinase 1 and 2; Gal‐3, galectin‐3; HPRT, hypoxanthine‐guanine phosphoribosyltransferase; IL, interleukin; MAPK, mitogen‐activated protein kinase; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa B; Runx2, runt‐related transcription factor 2; Sox‐9, SRY (sex‐determining region Y)‐box 9; α‐SMA, alpha‐smooth muscle actin; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; VICs, valvular interstitial cells.
