Figure 2.
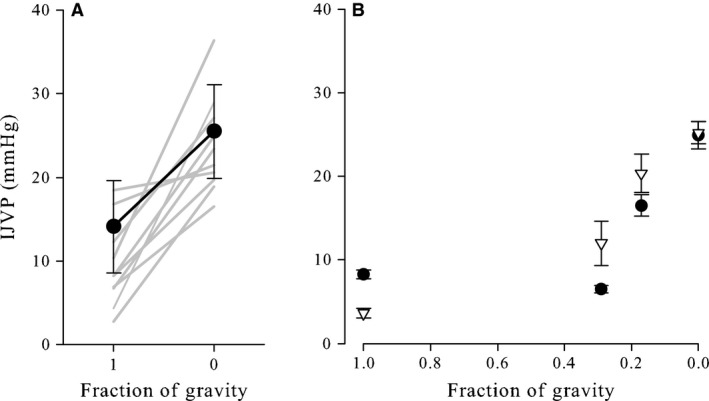
(Panel A) Mean (±standard deviation) internal jugular venous pressure (IJVP) was significantly lower (P ≤ 0.001) when supine before flight (Earth gravity, 1G) than during parabolic flight‐induced periods of weightlessness (0G). Individual results (n = 11) are displayed as gray lines. (Panel B) IJVP appeared to increase as gravitational load decreased from 1 g to 0G in two subjects during parabolic flight. Data from individual subjects are represented as mean ± standard deviation of 3–5 IJVP measurements.
