Figure 3.
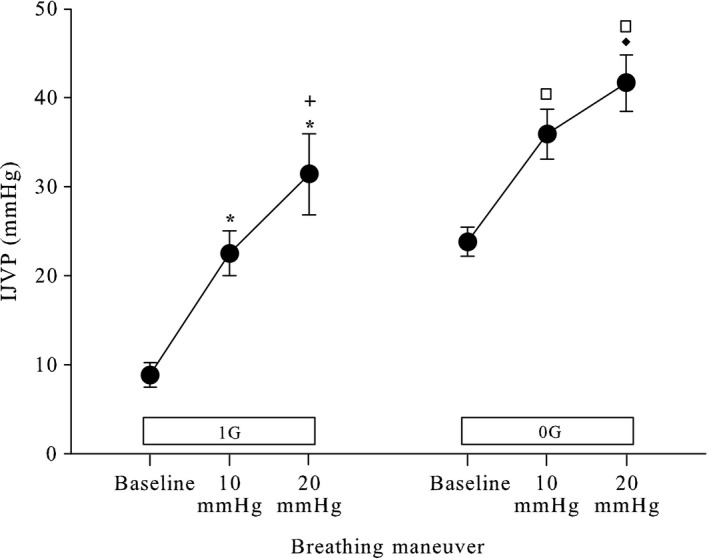
Mean (± standard deviation) internal jugular venous pressure (IJVP) assessed in 1G and 0G while conducting breathing maneuvers with expiratory pressures of 10 and 20 mmHg. 1G expiratory pressures elicited an increase in noninvasively measured IJVP that roughly approximated the change in intrathoracic pressure created by breathing maneuvers. (* <0.001 vs. 1G baseline, + =0.088 vs. 1G 10 mmHg, ♦ =0.066 vs. 0G 10 mmHg, □ <0.001 vs. 0G baseline).
