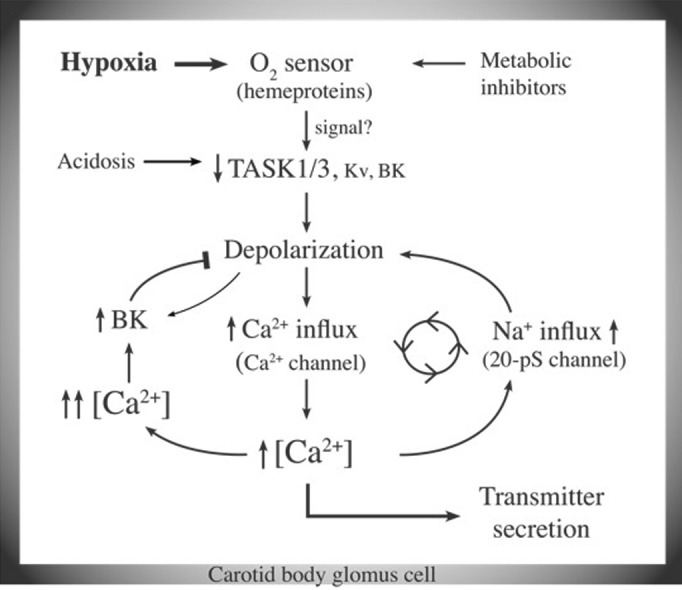
Figure 1. An updated model of O2 sensing by carotid body glomus cells. Hypoxia inhibits K+ channels such as TASK via an O2 sensor. The depolarization opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and elevates [Ca2+]i. Rise of [Ca2+]i begins to increase Na+ influx via the 20-pS channel, and initiates a feed-forward mechanism to maintain an optimal level of [Ca2+]i during moderate to severe hypoxia. Further increase in [Ca2+]i is prevented by activation of BK that opposes depolarization.
