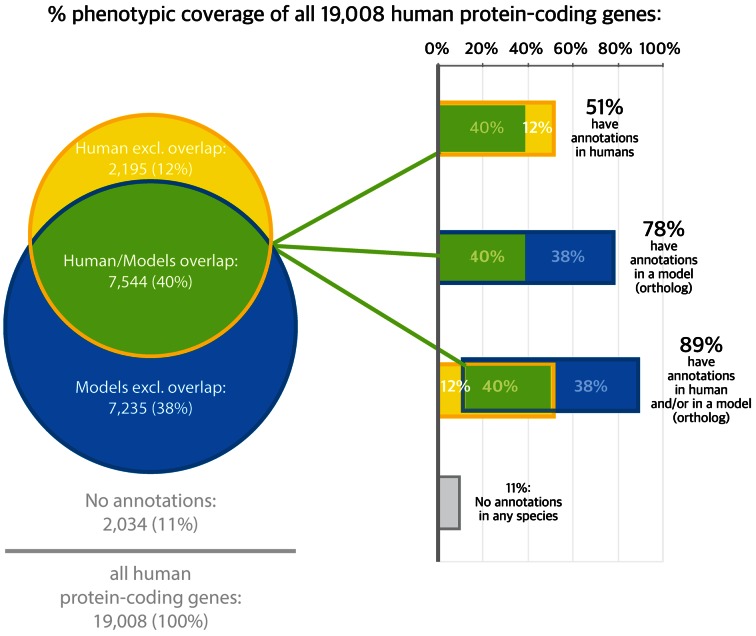
Figure 1.
The phenotype annotation coverage of human coding genes. Yellow bars show that 51% of those genes have at least one phenotype association reported in humans (HPO annotations of OMIM, ClinVar, Orphanet, CTD and GWAS). The blue bars show that 58% of human coding genes have orthologs with causal phenotypic associations reported in at least one non-human model (MGI, Wormbase, Flybase and ZFIN). The green bars show that 40% of human coding genes have annotations both in human and in non-human orthologs. There are phenotypic associations from humans and/or non-human orthologs that cover 89% of human coding genes.