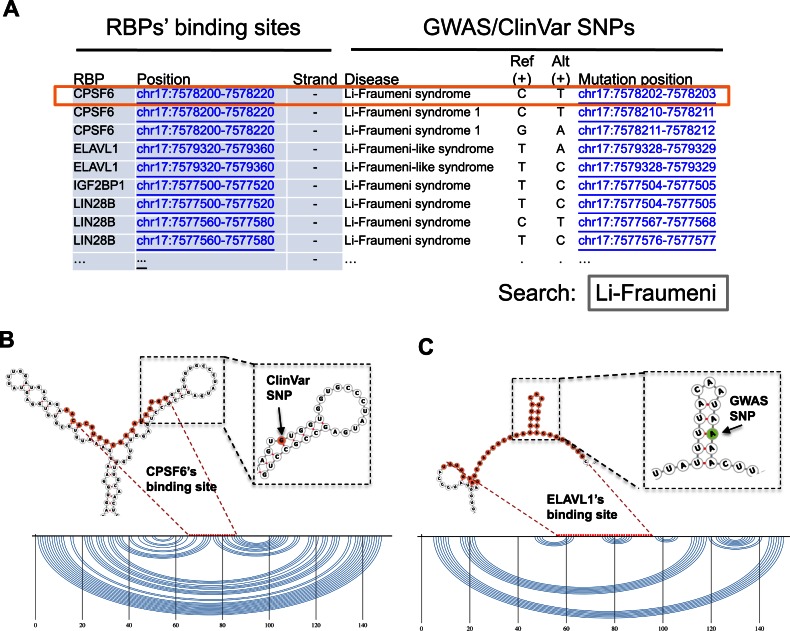
Figure 4.
Local structures of RBP binding sites on TP53. (A) Users can search for RBP binding sites on TP53 that are associated with disease SNPs by searching for the disease name (‘Li-Fraumeni syndrome’ as an example here) in the table on the server. (B) Predicted local secondary structure centered on a CPSF6 binding site. The local secondary structure around a Li-Fraumeni syndrome SNP (from the ClinVar database), which is a G-to-A mutation on the TP53's transcript (minus-strand), is magnified; it disrupts the base pair (G-C pair) in the hairpin's stem. Note that the mutation is a C-to-T mutation (box highlight in (A)) as annotated by ClinVar on the plus-strand. (C) Another predicted local secondary structure, centered on an ELAVL1 binding site, which contains a GWAS SNP that is an A-to-U mutation.