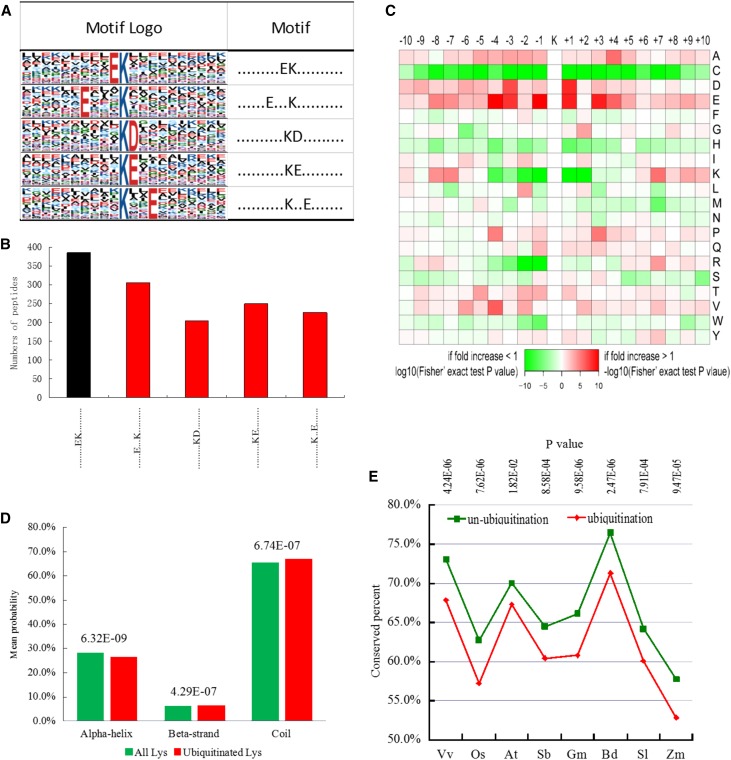
Figure 4.
Motif analysis of all the identified Kub sites in petunia. A, Ubiquitination motifs and the conservation of Kub sites. The height of each letter corresponds to the frequency of that amino acid residue in that position. The central K refers to the ubiquitinated Lys. B, Number of identified peptides containing ubiquitinated Lys in each motif. The red columns represent novel motifs. C, Amino acid sequence properties of ubiquitylation sites. The heat map shows significant position-specific underrepresentation or overrepresentation of amino acids flanking the modification sites. D, Predicted protein secondary structures near Kub sites. Probabilities for different secondary structures (coil, α-helix, and β-strand) of modified Lys residues were compared with the secondary structure probabilities of all Lys residues or all Ser/Thr/Tyr in all proteins identified in this study. E, Evolutionary conservation of ubiquitylated and nonubiquitylated Lys residues on protein orthologs in selected eukaryotic species: Vv, Vitis vinifera; Os, Oryza sativa japonica; At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Sb, Sorghum bicolor; Gm, Glycine max; Bd, Brachypodium distachyon; Sl, Solanum lycopersicum; Zm, Zea mays.