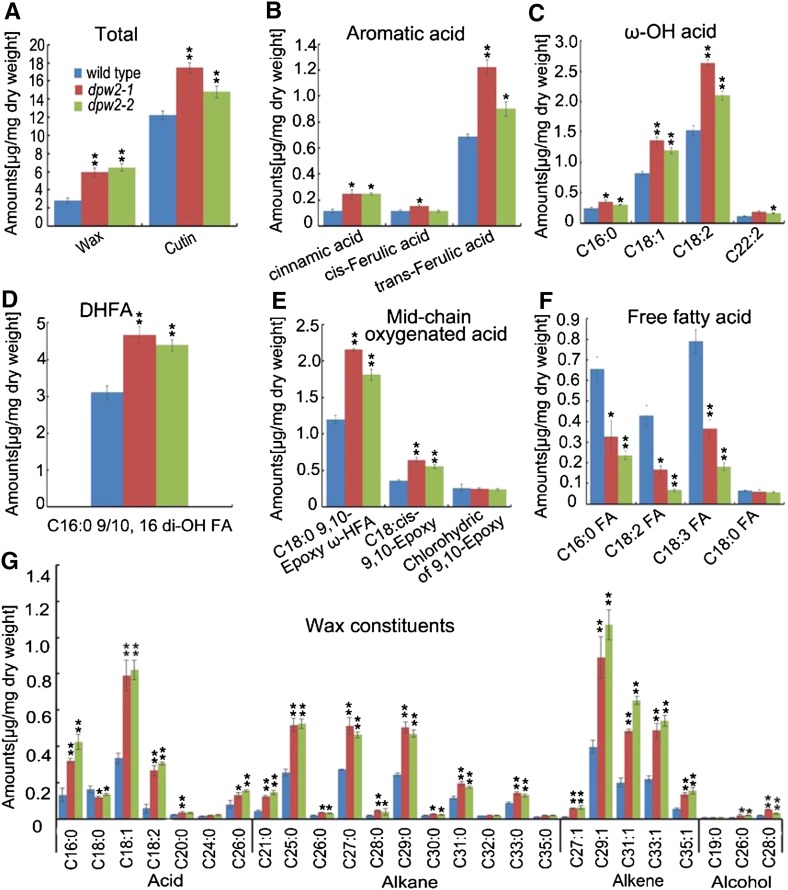
Figure 9.
Anther cutin and wax profiles in wild type and dpw2 mutants. A, Total wax and cutin amount. B, Comparison of the exact compositions of aromatic acid changes. C, Comparison of the exact compositions of ω-OH acid changes. D, Comparison of the compositions of C16:0 9/10, 16 di-OH fatty acid changes. E, Comparison of the exact compositions of midchain oxygenated acid changes. F, Comparison of the exact compositions of free fatty acid changes. G, Comparison of the wax constituents in anthers. Data are presented as the mean of three biological replicates ± sd. Error bars in A to G indicate sd (n = 3). Compound names in C to F are abbreviated as follows: C16:0 ω-HFA, 16-hydroxy-hexadecanoic acid; C18:1 ω-HFA, 18-hydroxy-oleic acid; C18:2 ω-HFA, 18-hydroxy-linoleic acid; C22:0 ω-HFA, 22-hydroxy-docosanoic acid; C16:0 9/10,di-OH FA, 9(10),16-dihydroxypalmitic acid; C18:0 9,10-Epoxy ω-HFA, 9(10)-epoxy-18-hydroxy-stearic acid; C18: cis-9,10 Epoxy, cis-9(10)-epoxy-stearic acid; Chlorohydric of 9,10 Epoxy, chlorohydric of 9(10)-epoxy-18-hydroxy-stearic acid; C16:0 FA, palmitic acid; C18:2 FA, linoleic acid; C18:3 FA, linolenic acid; C18:0 FA, octadecanoic acid. Compound names in G are abbreviated as follows: C16:0, palmitic acid; C18:0, octadecanoic acid; C18:1, oleic acid; C18:2, linoleic acid; C20:0, eicosanoic acid; C24:0, tetracosanoic acid; C26:0, hexacosanoic acid. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.