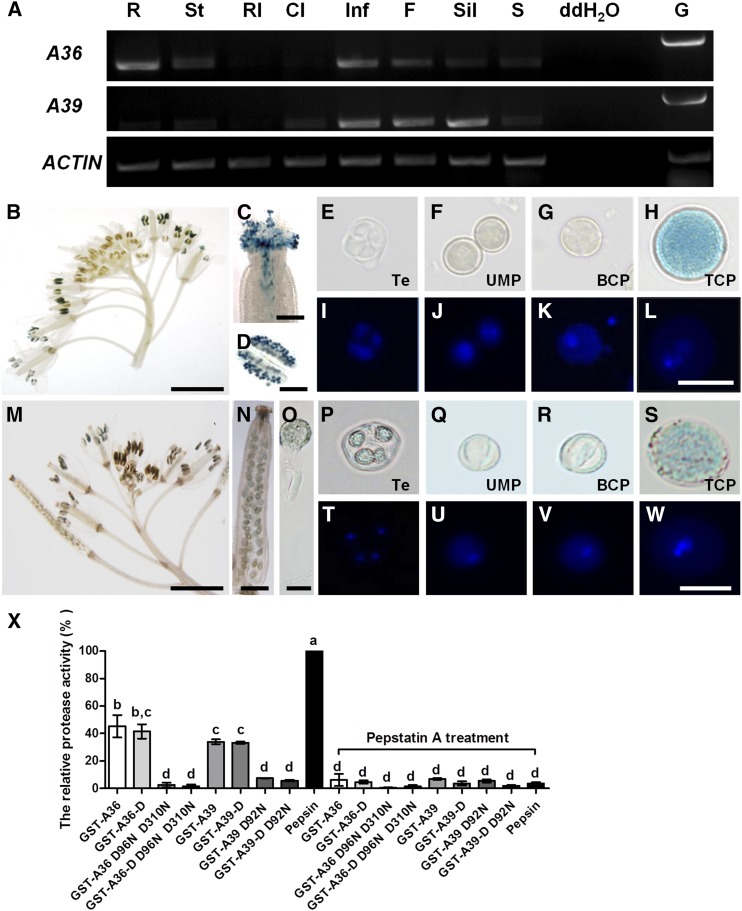
Figure 1.
A36 and A39 are highly expressed in mature pollen grains and growing pollen tubes and display aspartic proteolytic activity in vitro. A, Expression patterns of A36 and A39 in wild-type plants by RT-PCR. Total RNA was isolated from wild-type plants. ACTIN7 was taken as an internal control. Amplification was performed for 25 cycles for ACTIN7 and for 30 cycles for A36 (1,206 bp) and A39 (1,258 bp). R, Roots; St, stems; Rl, rosette leaves; Cl, cauline leaves; Inf, inflorescences; F, flowers; Sil, siliques; S, seedlings. Genomic DNA (G) as a positive control and distilled, deionized water (ddH2O) as a negative control also are presented. B to D, Expression pattern of A36 revealed by a promoter assay, showing GUS signals in inflorescence (B), stigma (C), and anther (D). Bars = 200 μm for B, 5 mm for C, and 20 μm for D. E to L, Developing male gametophytes by 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) and GUS staining. Te, Tetrad microspore (E and I); UMP, uninuclear microspore (F and J); BCP, bicellular pollen (G and K); TCP, tricellular pollen (H and L). Bar = 20 μm. M to O, Expression pattern of A39 revealed by a promoter assay, showing GUS signals in inflorescence (M), silique (N), and pollen tube (O). Bars = 5 mm for M, 500 μm for N, and 20 μm for O. P to W, Developing male gametophytes by DAPI and GUS staining. Te, Tetrad microspore (P and T); UMP, uninuclear microspore (Q and U); BCP, bicellular pollen (R and V); TCP, tricellular pollen (S and W). Bar = 20 μm. X, Semiquantitative assay of proteolytic activity. The GST-A36, GST-A36-D, GST-A39, GST-A39-D, and site-directed mutants GST-A36 D96N D310N, GST-A36-D D96N D310N, GST-A39 D92N, and GST-A39-D D92N were expressed in E. coli and purified in vitro. FITC-casein was used as the substrate. Equal amounts (375 ng) of GST fusion proteins and pork pepsin (positive control) were used, and the reaction was carried out at pH 5.4 and 22°C. Data were collected from three independent experiments. Error bars show se, calculated using one-way ANOVA; P < 0.05 by Tukey’s method.