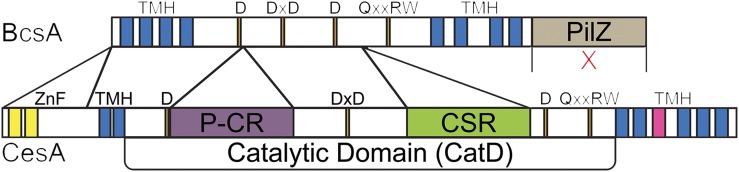
Figure 1.
Bar diagram of the domains and signature sequences of cellulose synthases in bacteria (BcsA) and plants (CesA). Like BcsA, CesA possesses four catalytic signature motifs (orange) containing conserved D, DxD, D, and Q/RxxRW residues. Plants differ from bacterial synthases by the absence of the PilZ activator domain (beige) and the addition of three unique domains, a RING-type zinc finger domain (ZnF; yellow) in the extended N terminus and the P-CR (purple) and CSR (green) domains inserted into the CatD. Recent work has indicated that CesA also may differ from BcsA in its number of transmembrane helices (TMH; blue), with BcsA possessing eight transmembrane helices and CesA likely possessing seven transmembrane helices, with the putative TMH5 (pink) hypothesized to occupy an interfacial orientation along the membrane (Slabaugh et al., 2016).