Figure 3.
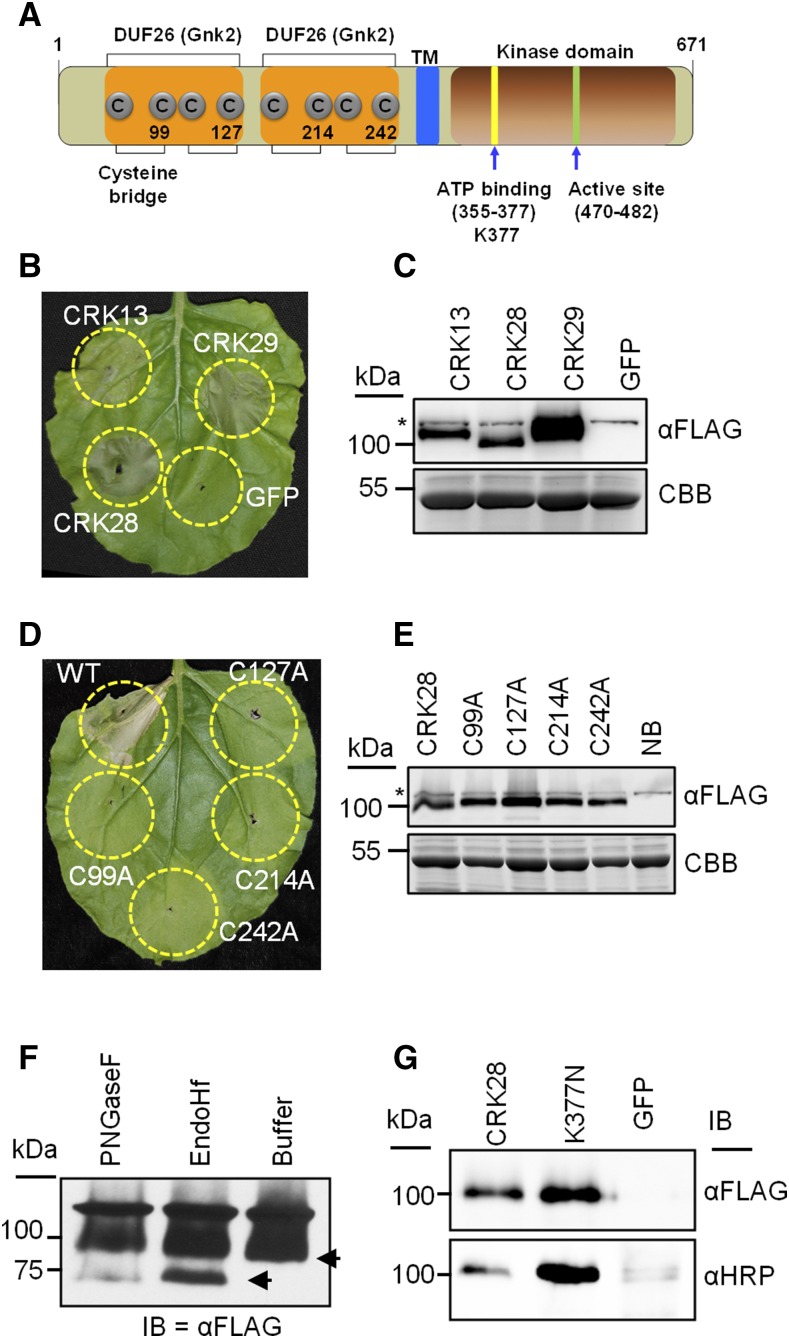
CRK28’s extracellular Cys residues are required for cell death induction in N. benthamiana. A, Diagram showing the general domain architecture of Arabidopsis CRK28. The N terminus includes a secretion signal with two predicted extracellular DUF26 domains (orange) and an intracellular kinase domain (brown). Predicted extracellular Cys residues and subdomains important for ATP binding and activity in other kinases are highlighted. TM, Transmembrane. Numbers correspond to amino acid residues. B, Cell death induced by transient expression of CRK13, CRK28, and CRK29 in N. benthamiana. A. tumefaciens containing 35S:CRK13-FLAG, 35S:CRK28-FLAG, 35S:CRK29-FLAG, and 35S:GFP was infiltrated into N. benthamiana leaves and photographed 48 hpi. C, Anti-FLAG immunoblot showing the expression of CRK13, CRK28, CRK29, and GFP 20 hpi in N. benthamiana. The bottom gel represents Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) stain to show protein loading. The asterisk shows an anti-FLAG cross-reacting band. D, Transient expression of 35S:CRK28-FLAG and four Cys mutants (C99A, C127A, C214A, and C242A) in N. benthamiana. Cell death was observed for wild-type CRK28, whereas no cell death was observed for Cys mutants. The leaf was photographed 48 hpi. E, Anti-FLAG immunoblot demonstrating the expression of CRK28 and the Cys mutants 20 hpi. NB, N. benthamiana (uninfiltrated). F, 35S:CRK28-FLAG was transiently expressed in N. benthamiana, and the detergent-soluble supernatant was used for PNGase F and Endo Hf enzymatic deglycosylation assays. Although the predicted molecular mass of CRK28 is 74.46 kD, by SDS-PAGE it is detected at 100 kD. G, Anti-HRP immunoblot (IB) demonstrating that CRK28 carries the complex N-linked glycan β-(1,2)-Xyl or α-(1,3)-Fuc. 35S:CRK28-FLAG and 35S:CRK28K377N-FLAG were expressed transiently in N. benthamiana and subjected to anti-FLAG IP. Mature glycosylation (in the Golgi) was detected using anti-HRP antibody. Anti-FLAG immunoblot analysis was performed to show the amount of IP loaded.