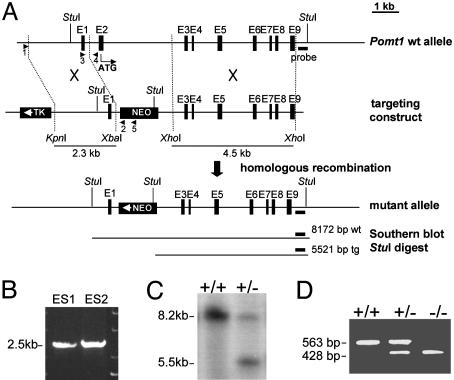
Fig. 3.
Targeted disruption of the Pomt1 gene. (A) Schematic representation of the targeting strategy: the genomic locus, the targeting construct, and the expected mutant Pomt1 allele after homologous recombination. Selectable markers: herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene (TK) and neomycin gene (NEO). The short (2.3-kb) and long (4.5-kb) arms for homologous recombination are represented. PCR primers are represented by arrows. (B) Primers 1 and 2 were used to identify two targeted embryonic stem clones after homologous recombination. (C) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from mouse tail tissue. Endogenous (8.2-kb) and targeted (5.5-kb) Pomt1 alleles. (D) PCR genotyping of embryos from timed matings. Primers 3 and 4 identify the endogenous allele, whereas primers 3 and 5 identify the targeted allele.