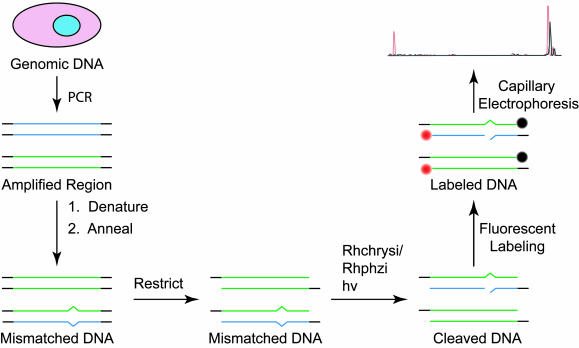
Fig. 2.
Strategy for detecting an SNP from genomic DNA in pooled samples. The portion of genomic DNA to be analyzed is selected and amplified by PCR. These PCR products are denatured and annealed to produce mismatches at the locations of heterozygous SNPs. The DNA is restricted to create a 3′ underhang to be labeled. The mismatched DNA is then treated with either Rhchrysi or Rhphzi and irradiated to cleave the DNA at the locations of the mismatches, corresponding to the SNP sites. The cleaved products are fluorescently labeled, followed by separation and detection by capillary electrophoresis.