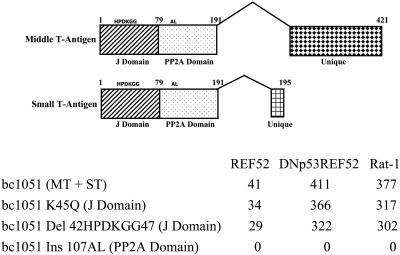
Fig. 3.
The J domain is not required for the PyMT induction of ARF or for PyST to block ARF signaling to p53. Mutations in the J and PP2A domains were incorporated into bc1051 genomic DNA and tested for transforming ability on REF52 cells, DNp53REF52 cells (REF52 cells containing a dominant-negative p53), and Rat-1 cells (in which neither ARF nor p21 is expressed, resulting in a compromised p53 response). The number of transformed colonies per microgram is shown for the transfecting bc1051 genomic DNA and bc1051 genomic DNAs containing various J domain and PP2A mutations. The J domain mutations were either a replacement of K with a Q at amino acid 45 in the J domain-binding region (K45Q) or a deletion of amino acids 42–47, which contain the complete J domain-binding region (Del 42HPDKGG47). The PP2A domain was mutated by the insertion of an AL at amino acid 107 (Ins 107AL) that has previously been shown to inactivate the ability of the Py T-antigens to bind PP2A (23). Because genomic DNA was used, the mutations were located in both the middle T-antigen (MT) and small T-antigen (ST) coding regions. At the top, the different splices to generate the middle and small T-antigens from the bc1051 genomic DNA are shown with the location of the mutations in the common J and PP2A domain regions. The numbers indicate the amino acid sequences of the different proteins. The location of the unique middle T-antigen and small T-antigen coding region is also shown.