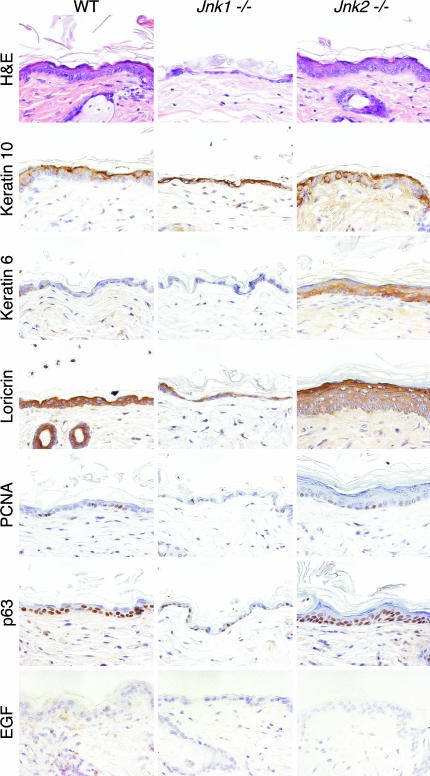
Fig. 5.
The epidermis of adult JNK-deficient mice is abnormal, with aberrant expression of markers of differentiation. H&E staining of skin sections from 16-week-old mice demonstrates that Jnk1–/– mice have a thin epidermis, whereas Jnk2–/– mice have a thick epidermis, compared with wild-type controls. Immunohistochemical staining for keratins 6 and 10, loricrin, PCNA, and p63 indicates abnormal expression in JNK-deficient animals. Markedly reduced expression of EGF mRNA in the skin of Jnk1–/– and -2–/– animals, compared with wild-type controls, was detected by in situ hybridization.