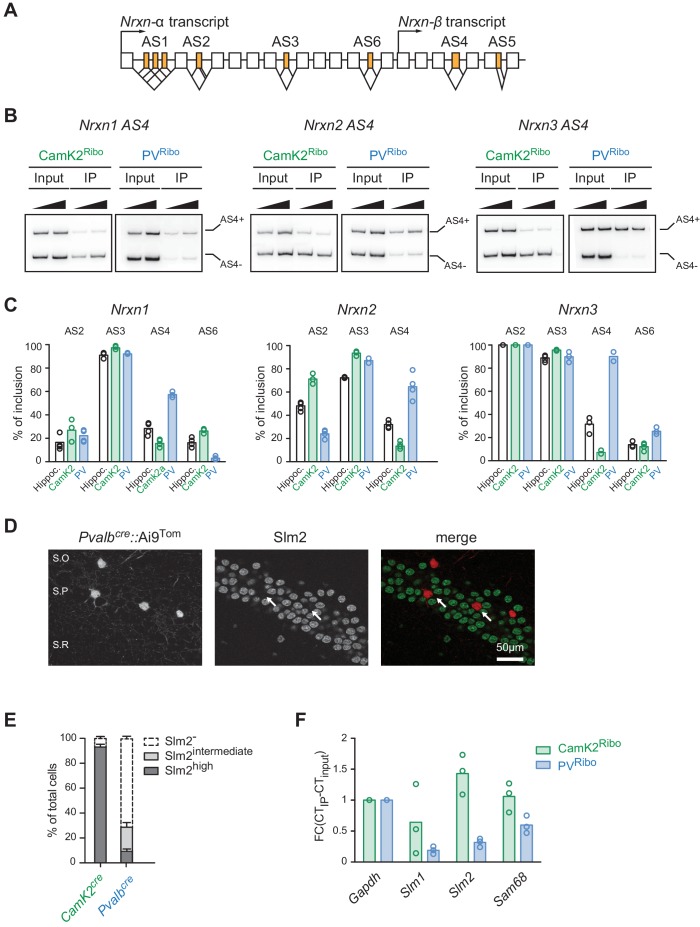
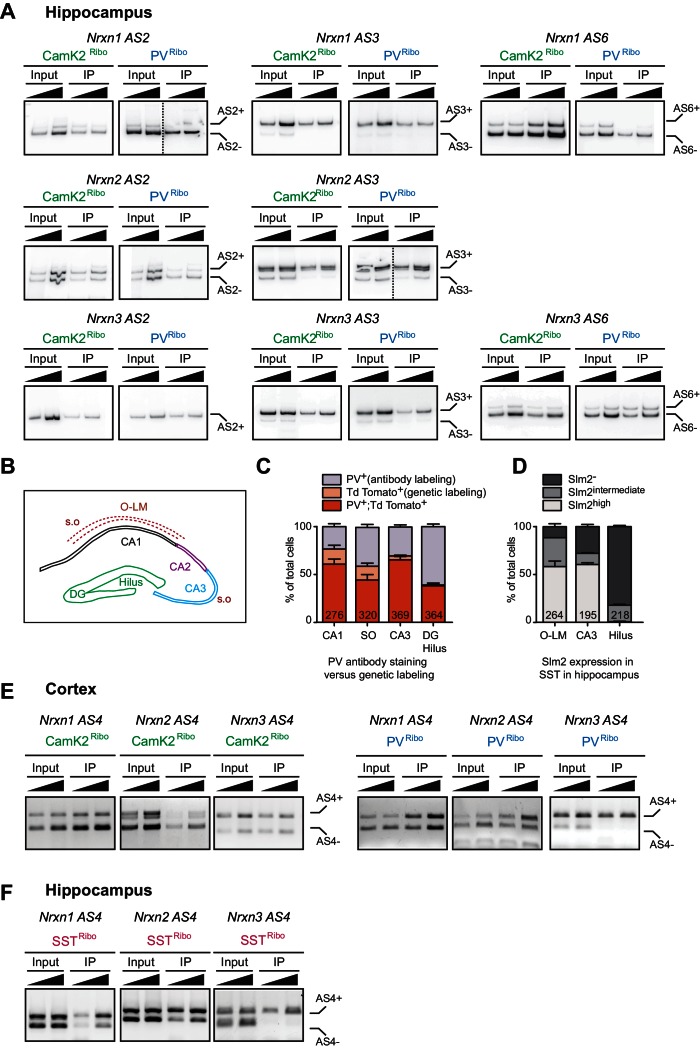
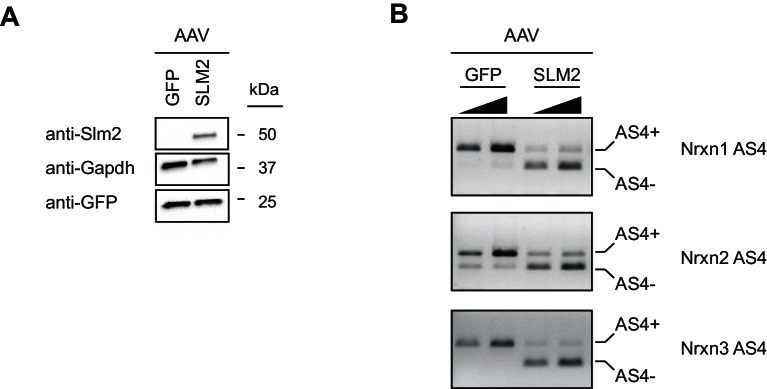
Figure 2. Cell type-specific alternative splicing.
(A) Schematic illustrating exon-intron structure of the Nrxn gene (example based on mouse Nrxn1). Alternatively spliced segments are numbered (AS1-6) and alternative exons are highlighted in orange, constitutive exons in white. (B) Analysis of alternative splicing pattern in total hippocampus (input), Camk2Ribo and PVRibo preparations. Radioactive PCR amplifications for Nrxn1,2,3 AS4. For each sample two PCR reactions with increasing cDNA input are shown. (C) Quantifications of alternative exon insertion rates at alternatively spliced segments (AS) 2,3,4, and six in Nrxn1,2,3 transcripts for total hippocampus (input), CamK2Ribo and PVRibo preparations. The insertion rates were measured by radioactive PCR with limiting cycle numbers. Raw data for the radioactive PCR amplifications are shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 1 (n= 3-4 independent mRNA preparations). (D) Expression of Slm2 in PV+ cells in mouse hippocampus (postnatal day 25–30) was examined using Pvalbcre::Ai9Tom mice. Dual immunohistochemistry on vibratome sections reveals high Slm2 expression in hippocampal pyramidal cells but no detectable expression in the majority of PV+ cells in and adjacent to the stratum pyramidale (S.O: stratum oriens, S.P: statrum pyramidale, S.R: stratum radiatum). (E) Quantification of the percentage of CamK2Ribo and Pvalbcre::Ai9Tom positive cells that show specific Slm2 immunoreactivity. (n = 5 mice for CamK2Ribo with a total of 2312 cells and five mice for Pvalbcre::Ai9Tom with a total of 244 cells, mean + SEM). (F) mRNA expression of STAR-family RNA-binding proteins was assessed by real-time qPCR in CamK2Ribo and PVRibo mRNA preparations (n = 3 independent mRNA preparations).