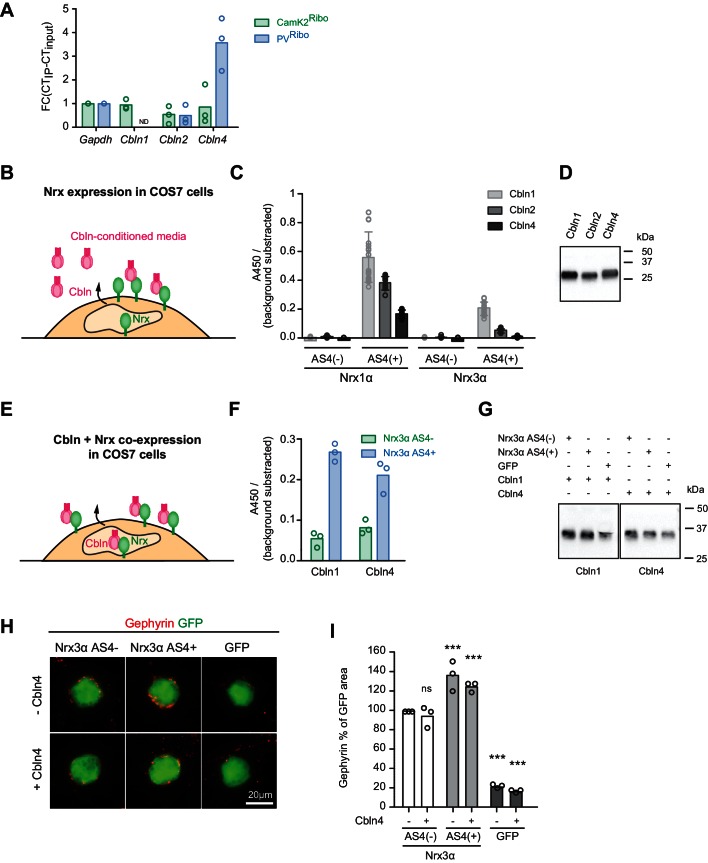
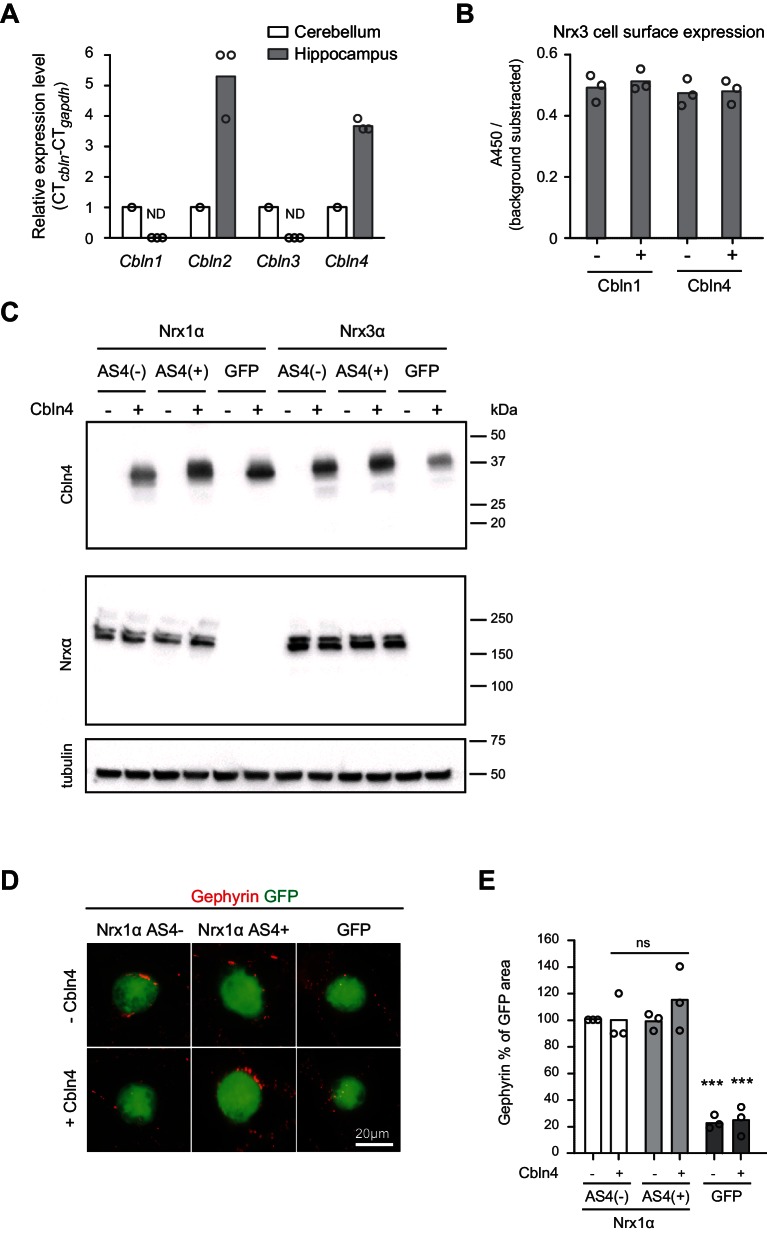
Figure 3. Regulation of Nrx3 interaction by AS4- splice insertions.
(A) Cbln1, 2, 3 and 4 mRNA expression level was assessed by real-time qPCR in CamK2Ribo and PVRibo preparations from mouse hippocampus. Transcript enrichment in the immunoisolate (IP) was calculated relative to the transcript level in the total hippocampus (input) and was normalized to Gapdh (n = 3 independent mRNA preparations). Note that Cbln1 mRNA could not be detected in the PVRibo mRNA preparation. ND: not detected. (B) Schematic for experimental setup: binding of Cbln1,2,4 proteins to COS7 cells expressing Nrx. Conditioned media containing V5-epitope-tagged Cbln proteins were applied to neurexin expressing cells and binding was determined using a HRP-mediated colorimetric reaction (see methods for details). (C) Quantification of Cbln-Nrx surface binding signals. The background was substrated from the signal. Single dots in the graph represent value of single well measurements (n = 20 measurements per condition, mean ± SD). (D) Expression level of V5-epitope tagged Cbln1, 2 and 4 in conditioned media from COS7 cells was probed by Western blotting analysis with anti-V5 antibodies. (E) Schematic for experimental setup: cell surface accumulation of Cbln1 or Cbln4 that were co-expressed with Nrx3α AS4 with or without splice insert in COS7 cells. The binding was determined using a HRP-mediated colorimetric reaction (see methods for details). (F) Quantification of cell surface accumulation of Cbln-Nrx. Signals were background subtracted and quantified from three independent experiments (n = 3 independent cell cultures). (G) Expression of myc-epitope tagged Cbln1 and 4 was probed by Western blotting. (H) Heterologous cell assays comparing synaptogenic activities of Nrx3 splice variants in presence and absence of Cbln4. HEK293 cells co-expressing Cbln4 with Nrx3α (with or without AS4 insertion) or GFP were introduced into cultures of hippocampal neurons and inhibitory postsynaptic structures were visualized by immunostaining with anti-gephyrin antibodies (red). (I) The density of gephyrin-positive structures, relative to the HEK293 cell area (GFP-positive) was quantified (n = 3 independent cultures,with ≥39 and 20 cells analyzed per condition for Nrx and GFP, respectively, mean ± SEM, Dunnet’s multiple comparison test, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05, [ns] not significant).