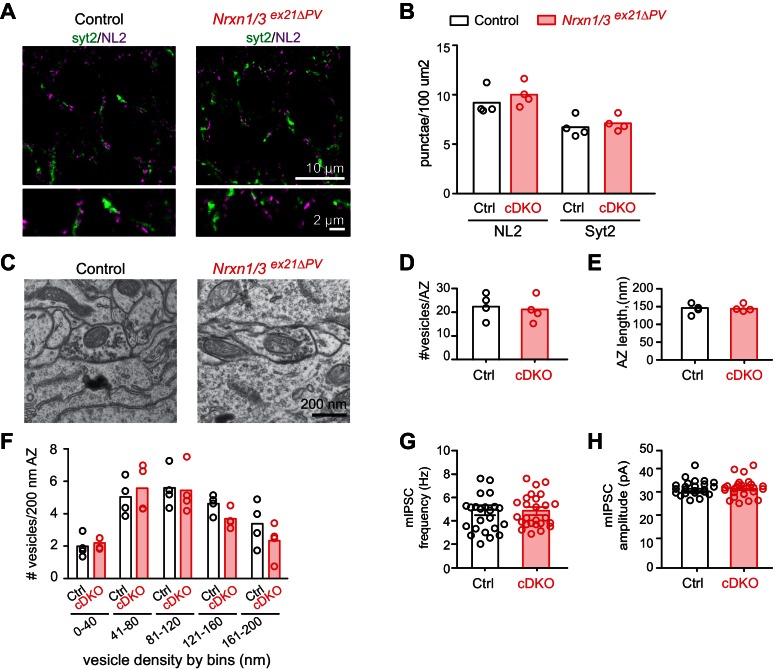
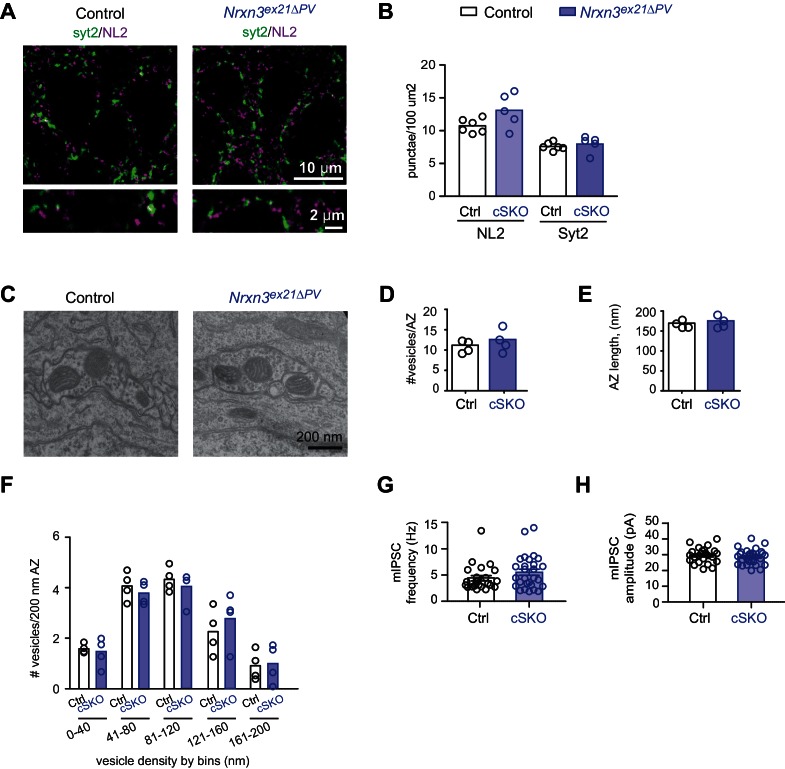
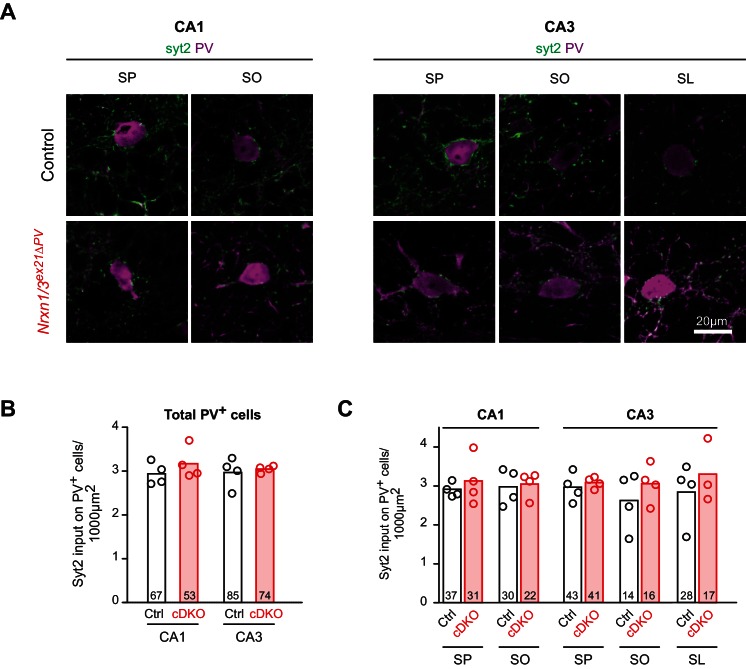
Figure 5. Analysis of PV+ specific Nrxn1/3ex21ΔPV conditional knock-out mice.
(A) The density of perisomatic GABAergic synapses in stratum pyramidale in CA1 of control and Nrxn1/3ex21ΔPV PV conditional double knock-out (cDKO) mice was examined by immunohistochemistry with anti-Neuroligin2 (NL2, in magenta) and anti-Synaptotagmin2 (Syt2, in green) antibodies at postnatal day 24–26. Note that Syt2 immuno-reactivity is specific for presynaptic terminals of PV+ cell synapses whereas NL2 is a common postsynaptic marker for most GABAergic synapses. Thus, only a fraction of NL2 puncta is apposed to Syt2-positive terminals. (B) The density of NL2 and Syt2 puncta per 100 μm2 of cell body area was quantified. Single dots in the graph represent means of respective synapse markers per animal (n = 4 mice per genotype). (C) Ultrastructure of inhibitory synapses in CA1 stratum pyramidale of littermate controls and Nrxn1/3ex21ΔPV mice. Presumptive PV+ cell perisomatic termini were identified by the presence of large mitochondria in the synapses apposed on the membrane of the soma and by their morphology (Takács et al., 2015). (D) Average vesicle numbers per active zone and (E) average active zone length in nm. Single dots in the graph represent means per animal (n = 4 mice for each genotype, ≥76 synapses). (F) Average number of vesicles located in 40 nm bins with increasing distance from the active zone normalized to 200 nm active zone length. Single dots in the graph represent means per animal (n = 4 mice for each genotype, ≥76 synapses). (G) mIPSC frequency and (H) amplitude in control and Nrxn1/3 ex21ΔPV mice. The recordings were performed in parallel with littermate controls. Single dots in the graph represent single cells (n = 3 control and 4 Nrxn1/3ex21ΔPV mice, mean ± SEM).