Figure 6.
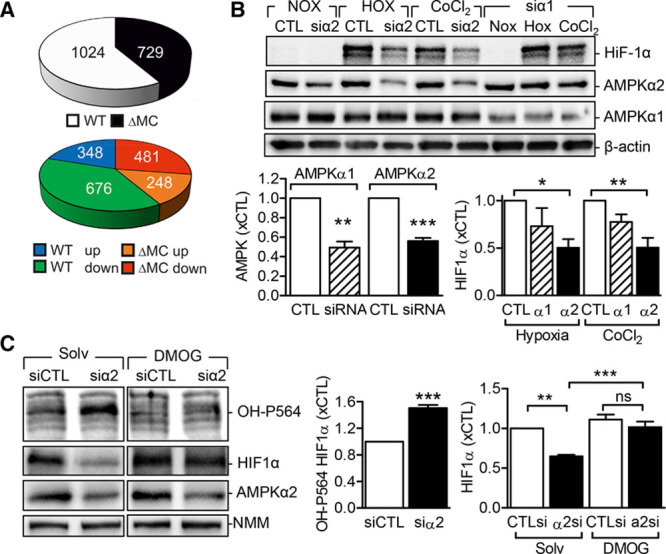
Link between AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) α2 and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α). A, Pie charts depicting significantly regulated proteins in neutrophils from wild-type (WT) and AMPKα2ΔMC (ΔMC) mice after 16-h exposure to hypoxia. Upper: total number of significantly regulated proteins. Lower: number of significantly up- and downregulated proteins. B, HIF-1α levels in HEK293 cells transfected with a control siRNA (CTL) or siRNA directed against AMPKα1 (siα1) or AMPKα2 (siα2) and then either maintained under normoxic conditions, exposed to hypoxia (1% O2, 6 h) or stimulated with CoCl2 (150 µmol/L, 6 h). Graphs summarize data from 5 independent experiments. C, HEK293 cells transfected with a control siRNA (siCTL) or siRNA-directed against AMPKα2 (siα2) were exposed to hypoxia in the presence of solvent (Solv) or dimethyloxalylglycine (DMOG; 1 mmol/L) for 16 h. HIF-1α levels and its hydroxylation on proline 564 (OH-P564) were analyzed by Western blotting (n=9–12 per group). The break in the blots indicates that nonadjacent lanes in the same Western blot are presented. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
