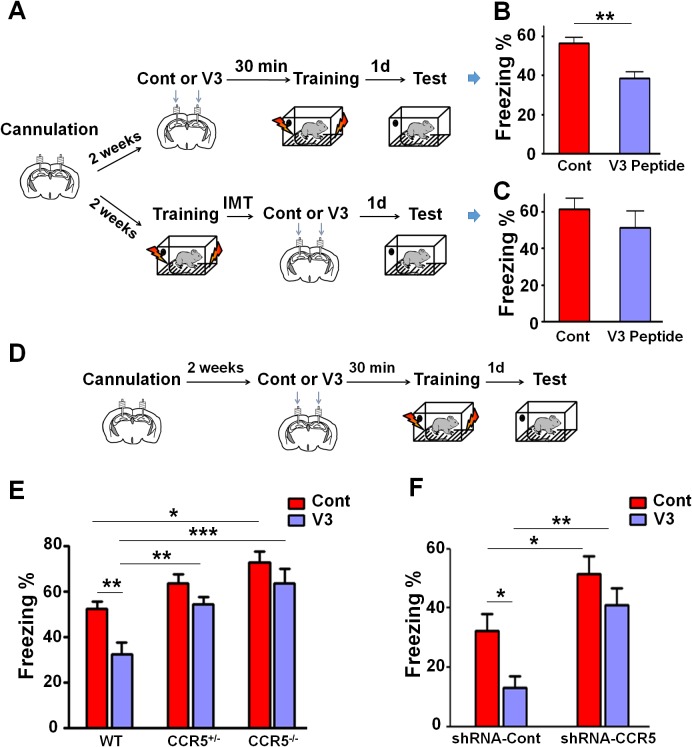
Figure 10. Both Ccr5 knockout and knockdown protect against gp120 V3 peptide induced memory deficits.
(A) Schematic of V3 peptide infusion and fear conditioning for the experiments shown in B and C. (B) 30 min after V3 peptide infusion into hippocampus, C57BL/6N mice were trained with fear conditioning. V3 peptide caused contextual memory deficits (Cont n = 6, V3 n = 6; **p<0.01, Student’s t-test). (C) When V3 peptide was infused into hippocampus immediately after fear conditioning training, no difference was observed between the control group and the V3 peptide group (Cont n = 10, V3 n = 10). (D) Schematic for experiments shown in E and F. (E) 30 min after V3 peptide infusion into hippocampus, mice were trained with fear conditioning. V3 peptide caused contextual memory deficits in WT mice, but Ccr5 knockout protected against V3-induced memory deficits (WT/Cont n = 10, WT/V3 peptide n = 11, Ccr5+/-/Cont n = 8, Ccr5+/-/V3 peptide n = 11, Ccr5-/-/Cont n = 8, Ccr5-/-/V3 peptide n = 8; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, Two-way ANOVA). (F) V3 peptide caused contextual fear conditioning memory deficits in mice injected with shRNA-Cont AAV, but hippocampal Ccr5 knockdown protected against V3-induced memory deficits (shRNA-Cont/Cont n = 10, shRNA-Cont/V3 n = 9, shRNA-CCR5/Cont n = 10, shRNA-CCR5/V3 n = 9; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, Two-way ANOVA). Error bars indicate SEM.