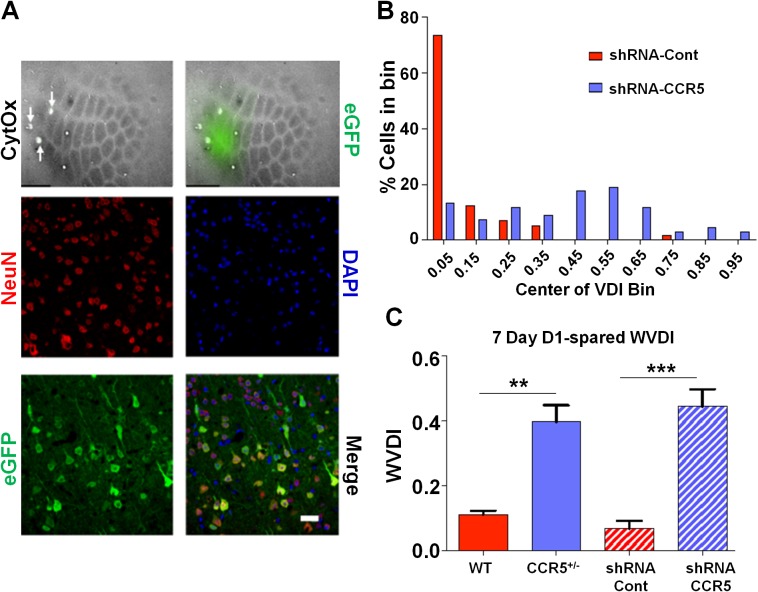
Figure 8. Viral knockdown of Ccr5 in barrel cortex enhances experience-dependent plasticity.
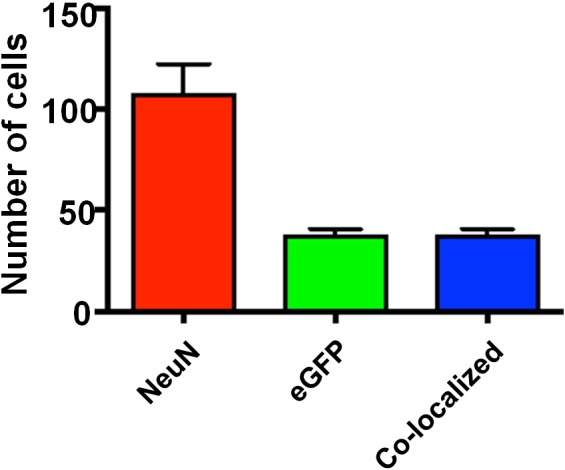
(A) Specificity and spread of viral infection. Interleaved slices processed for cytochrome oxidase (CytOx) confirmed viral location (GFP) over the recorded area of the barrel cortex. Arrows show lesions marking recording penetrations. Confocal images of the neuronal marker (NeuN) and viral expression (GFP) suggest that the shRNA is expressed exclusively in neurons. Scale bar = 20 µm. (B) Vibrissae dominance histogram after 7 days D1-spared single-whisker experience. Compared to control group, knockdown of Ccr5 leads to a shifted histogram (shRNA-cont n = 6; shRNA-CCR5 n = 6; p<0.001, Student’s t-test). (C) Weighted VDI values comparing Ccr5+/- mice with viral knockdowns. Viral knockdown has a similar effect to that of constitutive mutants after 7 days deprivation. Error bars indicate SEM.
Figure 8—figure supplement 1. Specificity of viral infection in the barrel cortex.