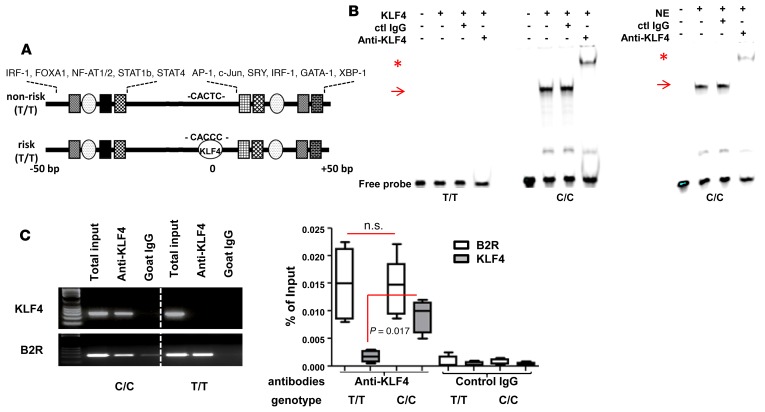
Figure 2. KLF4 binds to the risk SNP.
(A) Schematic of genomic sequence around SNP rs548234. Putative binding sites of various transcription factors are found upstream and downstream of the SNP, and the KLF4-binding site is identified only in risk SNP by using Transfac and oPOSSUM 3.0 programs. (B) KLF binding with the risk allele probe (C/C) not with nonrisk allele probe (T/T) by EMSA. Recombinant KLF4 (left) or nuclear extract (NE) (5 μg) (right) was incubated with either T/T or C/C probe. To identify specificity of binding, either control or anti-KLF4 Ab was added. Arrows indicate KLF4 binding and asterisks indicate supershift. A representative image is shown from 3 independent experiments. (C) In vivo binding of KLF4 to the risk allele. To perform the ChIP assay, MO-DCs from either risk allele carriers (C/C) or nonrisk allele carriers (T/T) were prepared and incubated with either control goat IgG or anti-KLF Ab overnight. After precipitation, qPCR and PCR were performed with a primer set that amplifies the SNP region. The B2R gene was amplified as a positive control. Percentage of input was calculated relative level to the total input. In the box-and-whisker plot, horizontal bars indicate the medians, boxes indicate 25th to 75th percentiles, and whiskers indicate 10th and 90th percentiles (n = 4). The nonparametric, Mann-Whitney test was used for statistics.