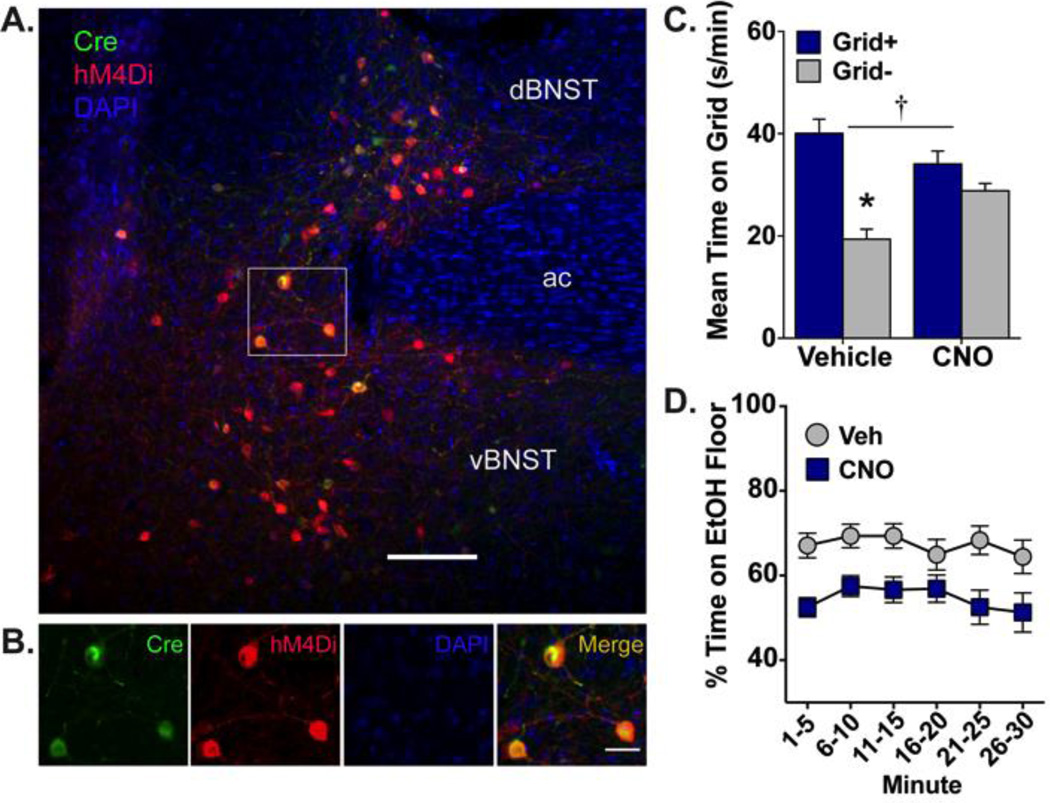
Figure 2. Ethanol-induced CPP expression is blocked by activation of hM4Di receptors selectively expressed in BNST-VTA cells.
(A) Heterologous expression of cre-dependent hM4Di (red; visualized by IF detection of mCherry) is observed in VTA-projecting neurons (green; visualized by IF detection of EYFP) of dorsal and ventral BNST. Nuclei are counterstained blue with DAPI; ac, anterior commissure; scale bar, 200 µm. (B) High magnification image of region outlined in white box above illustrating HSV-mediated cre expression (green), DIO-hM4Di expression (red), and their overlap (orange-yellow), with nuclei stained blue. Scale bar, 50 µm. (C) Mean (+SEM) time spent on the grid floor (in s/min) during 30-min preference test. VTA-projecting BNST neurons were inhibited via CNO (10 mg/kg)-mediated stimulation of hM4Di. Inhibition of BNST-VTA signaling blocked the expression of ethanol-induced CPP. † p≤0.001 interaction between drug and conditioning subgroup (Grid+ vs. Grid−); * p<0.001 between conditioning subgroups; n=13–15/subgroup. (D) Mean percent time (±SEM) spent on the ethanol-paired floor in 5-min intervals across the 30-min preference test. BNST-VTA inhibition reduced place preference in a consistent manner across the test.