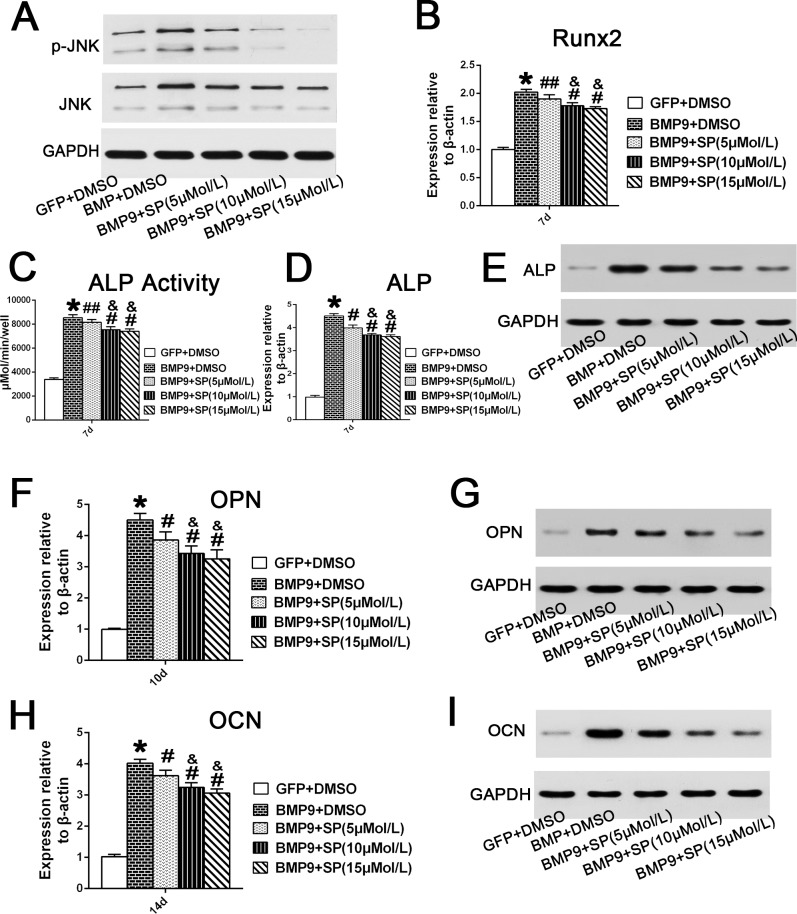
Fig 4. Inhibition of JNKs suppresses BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of hPDLSCs.
(A) Total JNK and phosphorylated JNK in Ad-BMP9-transfected hPDLSCs in the presence of SP600125 (5, 10, or 15 μM) were analysed by western blotting at day 4. (B) The Runx2 mRNA expression in BMP9-transfected cells was assessed by qRT-PCR assay after treatment with SP600125 (5, 10, or 15 μM) for 7 days. ‘‘*”, p<0.01 (vs. control group); ‘‘#”, p<0.01 (vs. BMP9 group); ‘‘##”, p<0.05 (vs. BMP9 group); “&”, p<0.01(vs. SP 5uM group); There was no significant difference between the SP 10 μM group and SP 15 μM group. (C) and (D) and (E) ALP activity in Ad-BMP9-transfected hPDLSCs in the presence of with SP600125 (5, 10, or 15 μM) was assessed by quantitative assay, qRT-PCR and western blotting assay at day 7. ‘‘*”, p<0.01 (BMP9 group vs. GFP control group); ‘‘#”, p<0.01 (vs. BMP9); ‘‘##”, p<0.05 (vs. BMP9 group); “&”, p<0.01(vs. SP 5 μM group). There was no significant difference between the SP 10 μM group and SP 15 μM group. (F) and (G) The mRNA expression and protein expression of OPN in BMP9-transfected cells after treatment with SP600125 (5, 10, or 15 μM) for 10 days, were analyzed by qRT-PCR and western blotting. ‘‘*”, p<0.01 (vs. control group); ‘‘#”, p<0.01 (vs. BMP9 group); “&”, p<0.01(vs. SP 5 μM group); There is no significance between SP 10 μM group and SP 15 μM group. (H) and (I) The mRNA expression and protein expression of OCN in hPDLSCs infected with BMP9 in the presence of SP600125 (5, 10, or 15 μM) for 14 days were analyzed by qRT-PCR and western blotting. ‘‘*”, p<0.01 (vs. control group); ‘‘#”, p<0.01 (vs. BMP9 group); “&”, p<0.01(vs. SP 5 μM group); There was no significant difference between the SP 10 μM group and the SP 15 μM group.