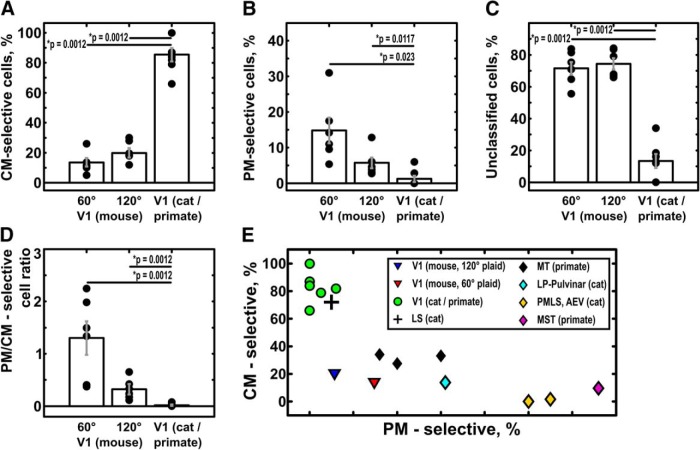
Figure 6.
Comparison of complex motion properties of mouse V1 and visual areas of primates and cats. WRS, Wilcoxon rank-sum test; 60°, mouse area V1, 60° plaid stimulation (n = 6 animals); 120°, mouse area V1, 120° plaid stimulation (n = 6 animals); V1 (cat/primate), primate or cat area V1 (n = 7 studies); LS, lateral suprasylvian area; PMLS, posteromedial lateral suprasylvian area; AEV, anterior ectosylvian visual area. Error bars indicate the mean ± SEM. Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used to access the difference between groups. A, The percentage of component-motion-selective neurons in mouse V1 is considerably smaller than in primate and cat V1 [V1(p)] for both 60° and 120° plaids (p = 0.0012, WRS). B, The percentage of neurons showing pattern-motion selectivity in mouse V1 is significantly larger than in primate V1 for both 120° plaid (p = 0.0117, WRS) and 60° plaid (p = 0.0023, WRS). C, Mouse V1 shows a high percentage of cells that are direction selective but cannot be classified as either CM- or PM-selective. The content of unclassified cells in mouse V1 is significantly higher than in primate and cat V1 (120° plaid, p = 0.0012, WRS; 60° plaid, p = 0.0012, WRS). D, The ratio between PM-selective and CM-selective responses in mouse V1 significantly decreases with increasing cross-angle of the plaid (120° vs 60° plaid, p = 0.007, WRS) and is significantly different form near-zero values, found in primate V1 (primate V1 vs mouse V1, p = 0.0012, WRS; either cross-angle). E, The relationship between PM-selective and CM-selective responses in mouse V1 (60° plaid, red triangles; 120° plaid, blue triangles,), primate/cat V1 (green circles), thalamic nuclei (cyan rhomboids), and extrastriate visual areas of primates and cats (cross, cat area LS; yellow rhomboids, cat PMLS and AEV; black rhomboids, primate MT; violet rhomboids, primate MST). The ratio of PM- and CM-selective responses places mouse V1 in between primate/cat V1 and primate/cat extrastriate areas [apart from cat area LS (cross), which shows properties close to cat area V1].