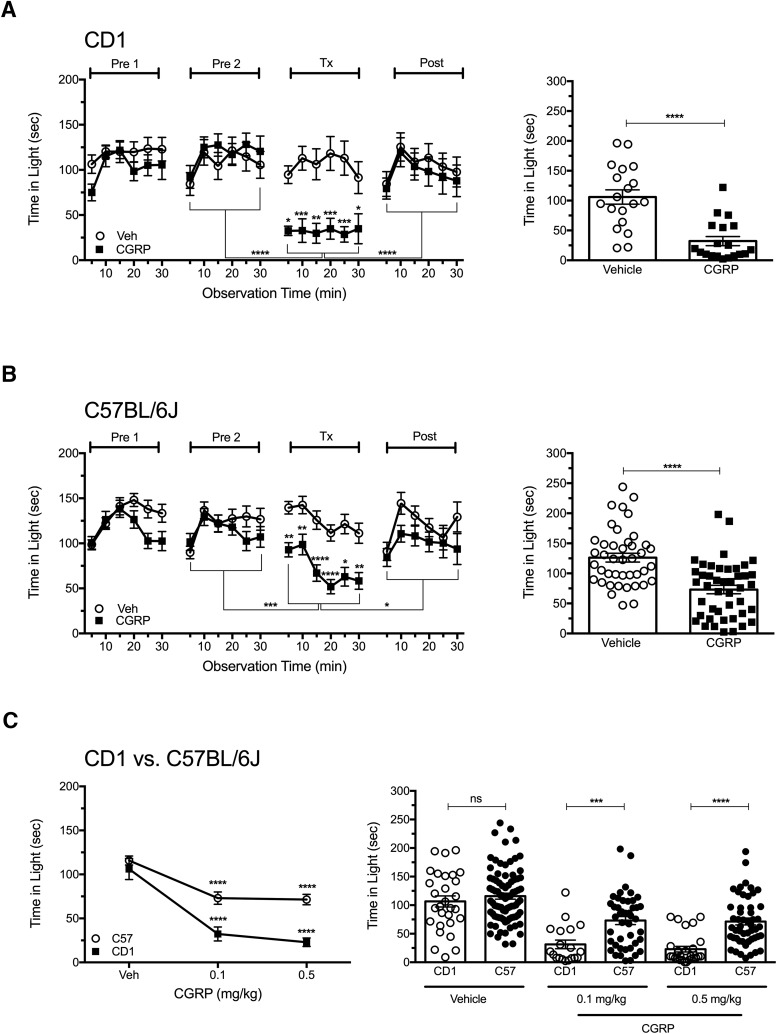
Figure 1.
Peripheral CGRP elicits light aversion in two strains of wild-type mice. A, Time spent in the light zone by CD1 mice during sequential exposures in the light/dark chamber at 2.7 × 104 lux (left). Mice were preexposed to the chamber twice (Pre1, Pre2) at 3 d intervals to reduce exploratory drive, then treated with vehicle (Veh, n = 19) or 0.1 mg/kg CGRP (n = 19) on treatment day (Tx), followed by a Post measurement. The mean ± SEM is shown, with significance indicated for comparisons of vehicle to CGRP at each time point and comparisons of Tx with Pre2 and Post indicated by brackets, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Right panel shows the mean time (±SEM) in light per 5 min interval for individual mice on treatment day, ****p < 0.0001. Data are from 2 independent experiments. B, Time spent in the light zone by C57BL/6J mice at 2.7 × 104 lux (left). Mice were treated as described in A with vehicle (Veh, n = 42) or 0.1 mg/kg CGRP (n = 44). Right panel shows the mean time (±SEM) in light per 5 min interval for individual mice on treatment day, ****p < 0.0001. Data are from four independent experiments. C, Dose-dependent effect of CGRP on time in light in CD1 and C57BL/6J (C57) mice (left). Mice were treated with vehicle (CD1, n = 29, 5 experiments; C57BL/6J, n = 83, 8 experiments), 0.1 mg/kg CGRP (CD1, n = 19, 2 experiments; C57BL/6J, n = 44, 4 experiments), 0.5 mg/kg CGRP (CD1, n = 28, 3 experiments; C57BL/6J, n = 51, 4 experiments). CGRP-treated C57BL/6J and CD1 mice spent significantly less time in the light at 0.1 and 0.5 mg/kg compared with vehicle (****p < 0.0001). Right panel shows the mean time (±SEM) in light per 5 min interval for individual CD1 and C57BL/6J mice on treatment day. CD1 mice spent significantly less time in the light compared with C57BL/6J mice at both 0.1 mg/kg CGRP (***p < 0.001) and 0.5 mg/kg CGRP (****p < 0.0001) and were not significant (ns) with vehicle.