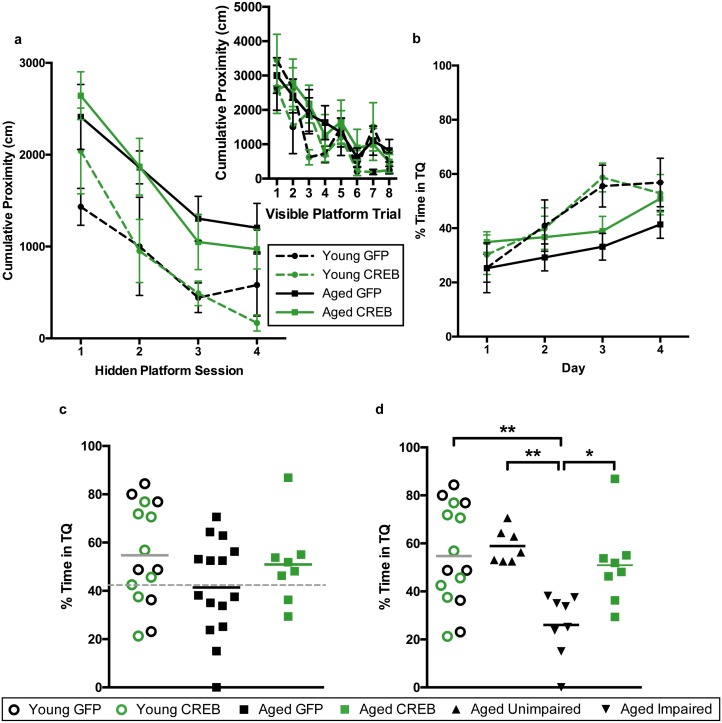
Figure 4. AAV-CREB ameliorates age-related spatial memory deficits on a more difficult water maze task.
(a) Performance on visible platform over eight trials (inset), and hidden platform over 4 sessions of training (three trials each session; one session per day) for young animals and aged animals that received control AAV-GFP, or AAV-CREB virus (n = 7, 8, 15, 8). All animals were capable of learning the visible and hidden platform task. While young animals performed better than aged on hidden platform training, no virus-based differences were observed. (b) Performance of young and aged animals that received AAV-GFP or AAV-CREB on probe trials run 1 hr after each session of hidden platform training (n = 7, 8, 15, 8). A difference was found between young and aged animals, but no effect of virus was observed. (c) Aged rats given control AAV-GFP vector trended towards worse performance on a probe test conducted 1 hr after the last hidden platform training session. Dashed line indicates the average performance of young rats that successfully learned minus 1 SD. (d) Aged rats classified as aged impaired (AI: n = 8) performed significantly worse on the probe test conducted on day 4 of hidden platform training as compared to young adult (n = 15), aged unimpaired (AU: n = 7) and aged rats given AAV-CREB (n = 8). No significant differences were observed between young adult, AU and aged CREB rats. Results in a and b represent mean ± SEM, horizontal bars in c, d represent mean.