Figure 6.
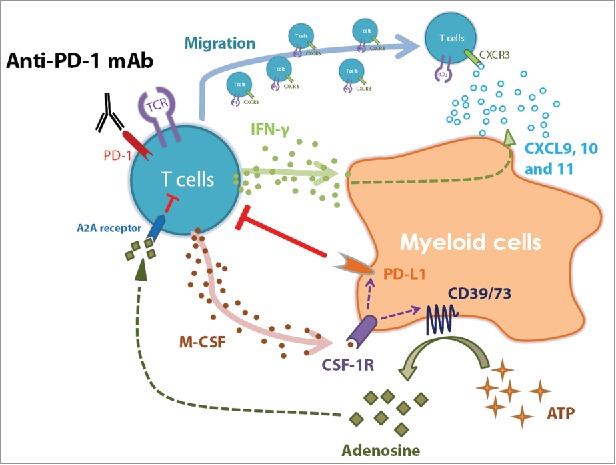
Regulation of myeloid cells by activated T cells in response to anti-PD-1 therapy. The graph summarizes the major findings of this study. Anti-PD-1 antibody treatment results in the release of IFNγ by activated T cells and re-activates myeloid cells to produce chemokines CXCL9, 10, and 11, which recruit T cells via CXCR3 signaling. At the same time, activated T cells secret M-CSF and enhance suppressive potentials of myeloid cells, such as upregulation of PD-L1 as well as CD39/CD73 expression. The adenosine catabolizing enzymes CD39/CD73 convert ATP to adenosine, which can inhibit T cells via A2A receptors.
