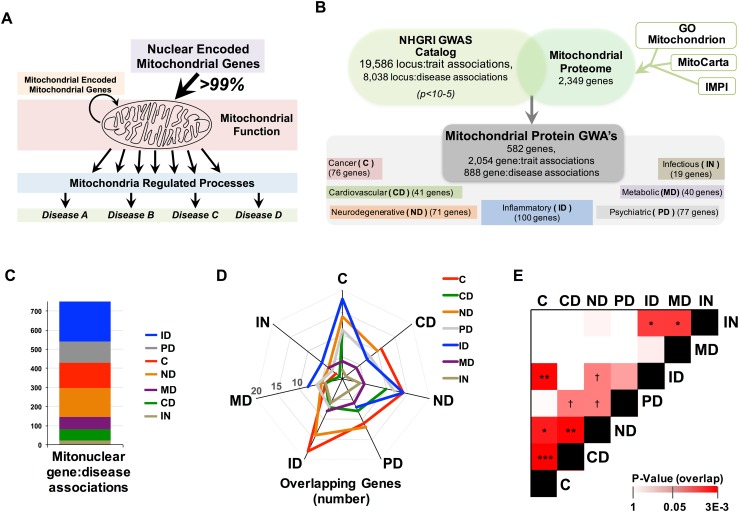
Fig. 1.
Nuclear encoded mitochondrial proteins associated with human disease by GWAS. a The majority of mitochondrial proteins are encoded by the nuclear genome and genetic variation in both the nuclear or mitochondrial genome influences disease risk. b The mitochondrial proteome was cross-referenced against the entire human GWAS catalog and mitonuclear gene:disease associations were analyzed by disease type. c Mitonuclear genes are strongly enriched for GWAS disease associations compared to the whole protein-coding genome. d Overlapping genes between each of the disease groups and e statistical assessment of the similarity (overlap) of mitonuclear gene signatures between diseases by hypergeometric distribution (see “Methods”, see also Fig. S1). † p = 0.05, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005 (C cancer, ID inflammatory disease, ND neurodegenerative disease, MD metabolic disease, CVD cardiovascular disease)