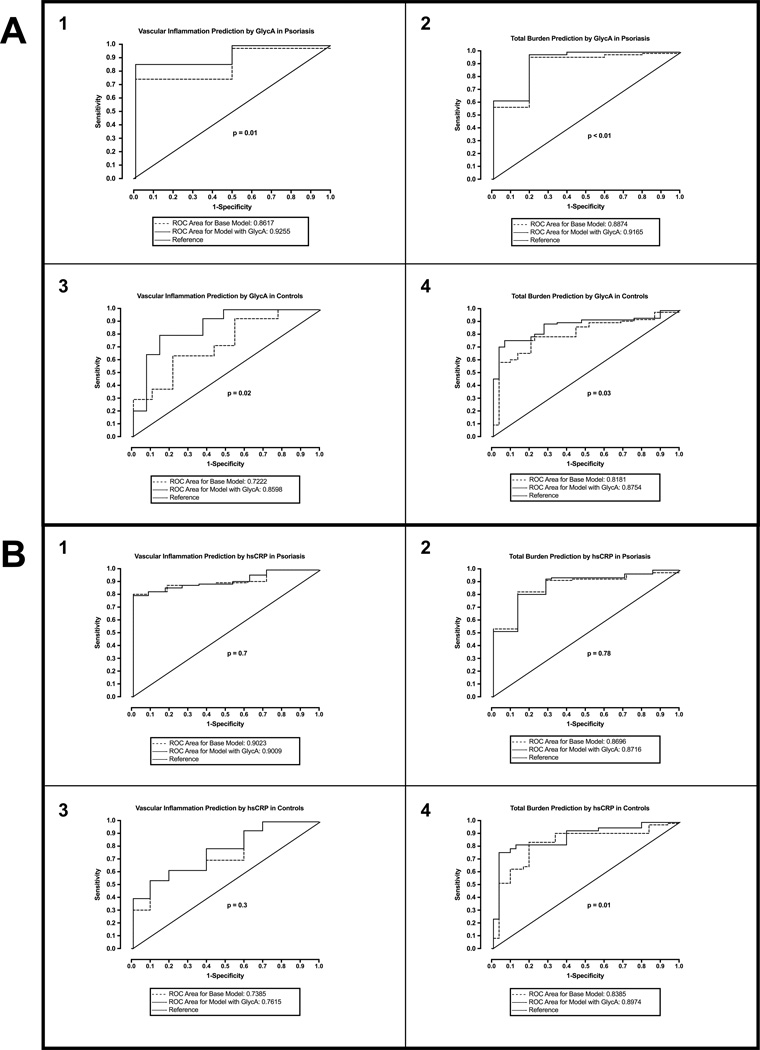
Figure 3.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves demonstrating incremental values added by GlycA and hsCRP: (A) ROC analyses demonstrate that GlycA adds value in predicting higher vascular inflammation and greater total burden of coronary artery disease in both psoriasis (1 and 2) and controls (3 and 4); (B) ROC analyses demonstrate that hsCRP adds value in predicting greater total burden of coronary artery disease (4) but not vascular inflammation (3) in controls, however, it fails to add any value in predicting vascular inflammation and coronary artery disease in psoriasis (1 and 2). Mean values of vascular inflammation and coronary artery disease burden were used to convert these continuous variables into dichotomous variables, such that values ≤ mean were designated as 1 and values < mean were designated as 0.