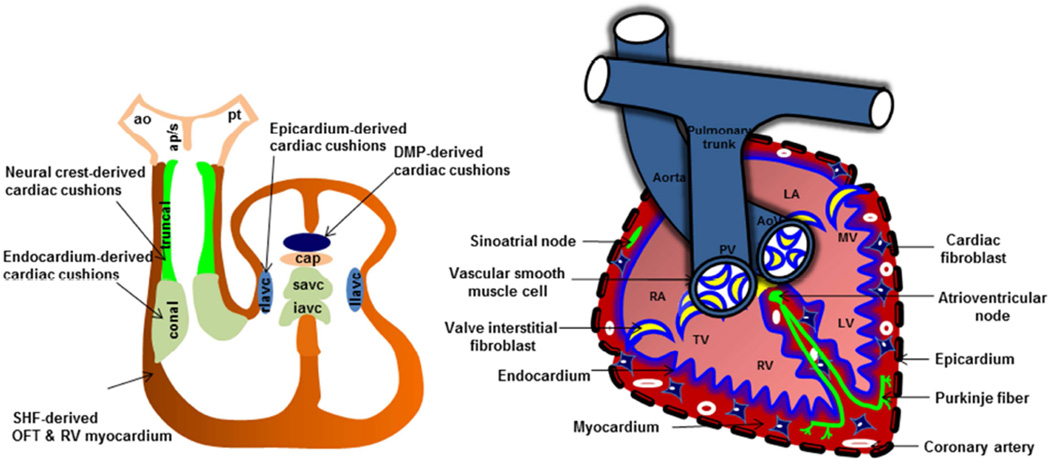
Figure 2. Cardiac remodeling and septation.
Myocardium, endocardium, cardiac fibroblasts, and epicardium are major cell types in the heart. Left side, Components of OFT and AV cushions are indicated. OFT contains well demarcated conal (endocardium-derived) and truncal (NC-derived) cushions. AV cushion mesenchymal complex contains superior and inferior AV cushions (predominantly EC-derived), right and left lateral AV cushions (rlavc, llavc) (with contributions from both epicardium and EC), mesenchymal cap (cap) and dorsal mesenchymal protrusion (dmp) (dorsal mesocardium-derived). Right side, fully septated 4-chambered heart. The valve annulus and vascular wall of the aorta and pulmonary trunk are predominantly comprised of smooth muscle cells. Heart valves predominantly contain valve interstitial cells. Endocardium/endothelium is the innermost layer, whereas epicardium is the outermost layer. Both ventricular and atrial regions contain myocardium and cardiac fibroblasts along with coronary vasculature. Purkinje fiber and atrioventricular and sinoatrial nodes constitute the cardiac conduction system. AoV, aortic valve; PV, pulmonary valve, RA, right atrium; TV, tricuspid valve; RV, right ventricle; LV, left ventricle; MV, mitral valve; LA, left atrium.