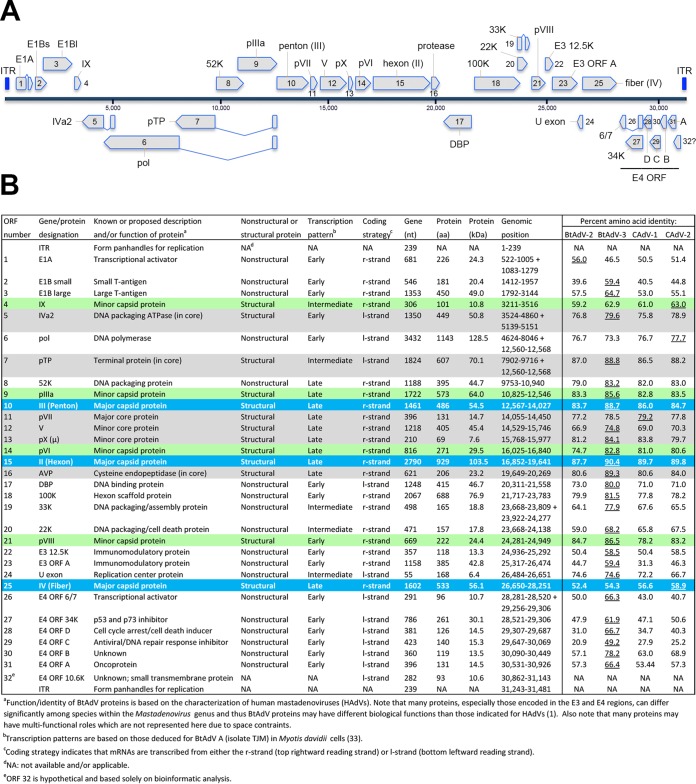
FIG 2.
Genomic organization of BtAdV 250-A. (A) The 31,481-nt genome of BtAdV 250-A is shown. The inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) found at the ends of the genome are highlighted in royal blue, with genes transcribed from left to right (from the top DNA strand) shown above the blue-gray solid line, and those transcribed from right to left (from the bottom DNA strand) are indicated below. Genes that are believed to be spliced are indicated by two genetic elements that are connected by adjoining lines in a “V” or “V” pattern. (B) The 31 ORFs identified in the BtAdV 250-A genome that share homology to other BtAdVs and canine mastadenoviruses (CAdVs) are shown. All 13 tentative structural proteins are highlighted with shading: (i) the three major capsid proteins—II (hexon), III (penton), and IV (fiber)—found on the particle surface (blue), (ii) four minor capsid/cement proteins—IIIa, VI, VIII, and IX—found on or just beneath the particle surface (green), and (iii) six core proteins—IVa2, V, VII, X, TP, and the adenovirus protease (AVP)—found internally (gray). The percent amino acid identity of the BtAdV 250-A proteins to other viruses was determined using the following GenBank accession numbers: BtAdV 250-A (KX871230), BtAdV A (NC_016895), BtAdV B (JN252129), CAdV A (CAdV-1) (AC_000003), and CAdV A (CAdV-2) (AC_000020). The virus sharing the highest degree of amino acid identity to BtAdV 250-A for each protein is underlined. A lowercase “p” preceding a protein's name (i.e., pTP, pIIIa, pVI, pVII, pVIII, and pX) indicates a precursor form of the protein that is subsequently cleaved by the AVP.