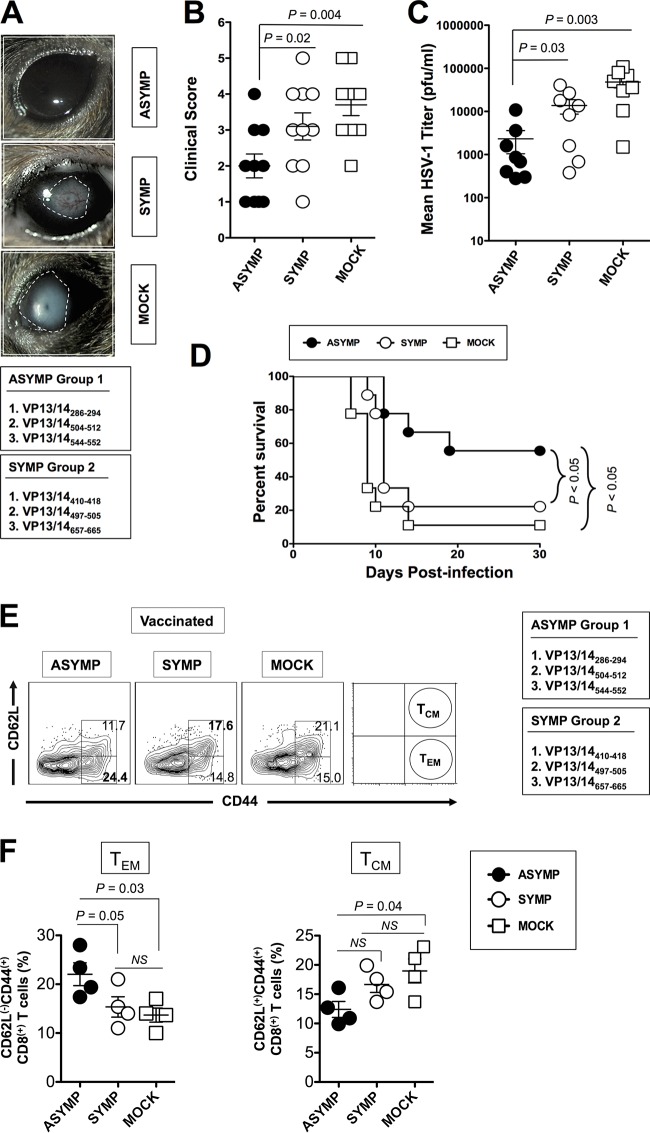
FIG 6.
Protective immunity against ocular herpes induced by ASYMP VP13/14 CD8+ TEM-cell epitopes in humanized HLA transgenic mice. Three groups of age- and sex-matched HLA Tg mice (n = 10 each) were immunized subcutaneously on days 0 and 21 with a mixture of ASYMP CD8+ T-cell peptide epitopes (VP13/14286–294, VP13/14504–512, and VP13/14544–552) and a mixture of SYMP CD8+ T-cell human epitopes (VP13/14410–418,VP13/14497–505 and VP13/14657–665). These were delivered together with a promiscuous CD4+ T-cell epitope (PADRE) emulsified in CpG1826 adjuvant. CpG1826 adjuvant alone was used for mock vaccination. Two weeks after the final immunization, all animals were challenged ocularly with 2 × 105 PFU of HSV-1 (strain McKrae). (A and B) The severity of herpetic eye disease was followed for 2 weeks after immunization and scored on a scale of from 1 to 5. (C) Virus titrations were determined from eye swab specimens collected on day 7 postinfection. (D) Survival was determined within a window of 30 days postchallenge. Corneas were harvested from each group, and the frequencies of CD44high CD62Llow CD8+ TEM cells and CD44high CD62Lhigh CD8+ TCM cells were analyzed by FACS using specific MAbs. (E) Representative data on the frequencies of CD8+ TEM and CD8+ TCM cells detected from the corneas of one protected ASYMP HLA Tg mouse, one nonprotected SYMP HLA Tg mouse, and one mock-immunized HLA Tg mouse. (F) Average frequencies of TCM and TEM CD8+ cells detected in the corneas of four ASYMP, four SYMP, and four mock-immunized HLA Tg mice. The results are representative of those from 2 independent experiments. The indicated P values, calculated using an unpaired t test, show statistically significant differences between ASYMP, SYMP, and mock-immunized mice.