Figure 4.
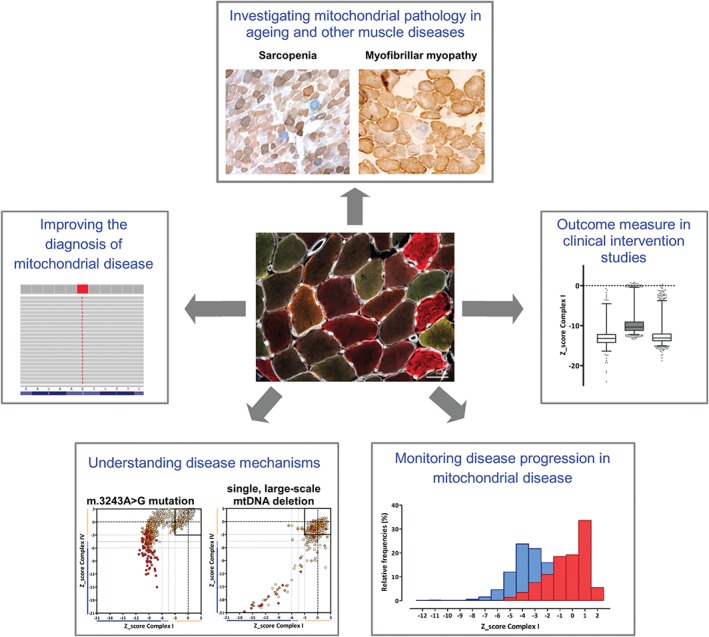
Current and future applications of a quantitative, quadruple OXPHOS immunofluorescence assay. Given its capacity to interrogate levels of both complex I and IV – and additional OXPHOS components – at a single muscle fibre level, we believe that the quadruple immunofluorescence assay can be applied to several areas of diagnostic and research activity in the laboratory to help investigate the role of mitochondrial biochemical defects 96. We are already implementing this methodology in a diagnostic setting, validating the assay with biopsies from patients showing a range of mtDNA‐related and nuclear genetic diagnoses of mitochondrial disease. The assay also shows promise as a powerful tool with which to investigate the mitochondrial pathological changes observed in ageing and other myopathies (e.g. myofibrillar myopathies 90), to investigate molecular disease mechanisms and mitochondrial disease progression, as well as providing an extremely sensitive outcome measure in clinical therapeutic intervention studies (e.g. pharmacological agents or exercise) aimed at improving muscle oxidative capacity in patients with mitochondrial disease.
